Multidimensional Engineering of Escherichia coli for Efficient Adipic Acid Synthesis From Cyclohexane
- PMID: 39960345
- PMCID: PMC11984861
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202411938
Multidimensional Engineering of Escherichia coli for Efficient Adipic Acid Synthesis From Cyclohexane
Abstract
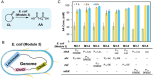
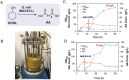
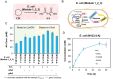
Adipic acid (AA), a key aliphatic dicarboxylic acid, is conventionally manufactured through energy-intensive, multi-step chemical processes with significant environmental impacts. In contrast, biological production methods offer more sustainable alternatives but are often limited by low productivity. To overcome these challenges, this study reports the engineering of a single Escherichia coli for efficient biosynthesis of AA starting from cyclohexanol (CHOL), KA oil (mixture of CHOL and cyclohexanone (CHONE)), or cyclohexane (CH). To start with, a comprehensive screening of rate-limiting enzymes is conducted, particularly focusing on cytochrome P450 monooxygenase, followed by the optimization of protein expression using strategies such as protein fusion, promoter replacement, and genome editing. Consequently, an engineered E. coli capable of efficiently converting either KA oil or CH into AA is obtained, achieving remarkable product titers of 110 and 22.6 g L-1, respectively. This represents the highest productivity record for the biological production of AA to date. Finally, this developed biocatalytic system is successfully employed to convert different cycloalkanes and cycloalkanols with varied carbon chain lengths into their corresponding dicarboxylic acids, highlighting its great potential as well as broad applicability for industrial applications.
Keywords: adipic acid; balance; biosynthesis; cascade pathway.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
[Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for adipic acid production].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2023 Jun 25;39(6):2375-2389. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.220992. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2023. PMID: 37401599 Chinese.
-
Biosynthesis of adipic acid in metabolically engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Microbiol. 2020 Dec;58(12):1065-1075. doi: 10.1007/s12275-020-0261-7. Epub 2020 Oct 23. J Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33095385
-
Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for producing adipic acid through the reverse adipate-degradation pathway.Metab Eng. 2018 May;47:254-262. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2018.04.002. Epub 2018 Apr 3. Metab Eng. 2018. PMID: 29625225
-
Biobased adipic acid - The challenge of developing the production host.Biotechnol Adv. 2018 Dec;36(8):2248-2263. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.10.012. Epub 2018 Oct 30. Biotechnol Adv. 2018. PMID: 30389426 Review.
-
Metabolic engineering strategies to bio-adipic acid production.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2017 Jun;45:136-143. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2017.03.006. Epub 2017 Mar 31. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28365404 Review.
References
-
- de Jong E., Higson A., Walsh P., Wellisch M., IEA Bioenergy, Task42 Biorefinery 2012, 34, 1.
-
- Castellan A., Bart J. C. J., Cavallaro S., Catal. Today 1991, 9, 237.
-
- Rios J., Lebeau J., Yang T., Li S., Lynch M. D. J., Green Chem. 2021, 23, 3172.
-
- Sato K., Aoki M., Noyori R., Science 1998, 281, 1646. - PubMed
-
- Hwang K. C., Sagadevan A., Science 2014, 346, 1495. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
