A VLP vaccine platform comprising the core protein of hepatitis B virus with N-terminal antigen capture
- PMID: 39961558
- PMCID: PMC7618004
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.141152
A VLP vaccine platform comprising the core protein of hepatitis B virus with N-terminal antigen capture
Abstract
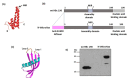
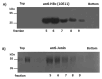
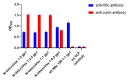
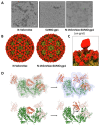
Nanoparticle presentation systems offer the potential to develop new vaccines rapidly in response to emerging diseases, a public health need that has become increasingly evident in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. Previously, we reported a nanoparticle scaffold system termed VelcroVax. This was constructed by insertion of a high affinity SUMO binding protein (Affimer), able to recognise a SUMO peptide tag, into the major immunodominant region of VLPs assembled from a tandem (fused dimer) form of hepatitis B virus (HBV) core protein (HBc). Here we describe an alternative form, termed N-VelcroVax, a VLP vaccine platform assembled from a monomeric HBc protein (N-anti-SUMO Affimer HBc 190) with the Affimer inserted at the N-terminus. In contrast to the tandem form of VelcroVax, N-VelcroVax VLPs were expressed well in E. coli. The VLPs effectively bound SUMO-tagged Junín virus glycoprotein, gp1 as assessed by structural and serological analyses. Cryo-EM characterisation of N-VelcroVax complexed with a SUMO-Junín gp1 showed continuous density attributable to the fused Affimer, in addition to evidence of target antigen capture. Collectively, these data suggest that N-VelcroVax has potential as a versatile next generation vaccine scaffold.
Keywords: ClearColi; HBcAg; Junín virus; Platform; Vaccine; Virus-like particle.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Amanna I, Slifka M. Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology. Springer International Publishing; 2018. Vaccination strategies against highly variable pathogens; pp. 1–30.
-
- Nandy A, Basak SC. Bioinformatics in design of antiviral vaccines. Encyclopedia of, Biomed Eng. 2019:280.
-
- Brenzel L, et al. Vaccine-preventable diseases. Disease control priorities in developing countries. 2006;2:389–412.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

