Acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF): the 'Kyoto Consensus'-steps from Asia
- PMID: 39961976
- PMCID: PMC11846769
- DOI: 10.1007/s12072-024-10773-4
Acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF): the 'Kyoto Consensus'-steps from Asia
Abstract
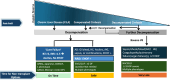
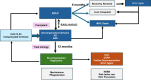
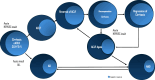
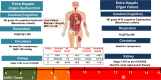
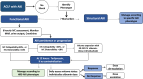
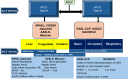
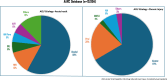
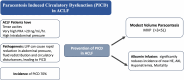
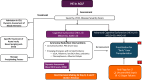
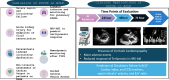
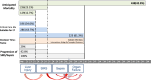
Acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) is a condition associated with high mortality in the absence of liver transplantation. There have been various definitions proposed worldwide. The first consensus report of the working party of the Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver (APASL) set in 2004 on ACLF was published in 2009, and the "APASL ACLF Research Consortium (AARC)" was formed in 2012. The AARC database has prospectively collected nearly 10,500 cases of ACLF from various countries in the Asia-Pacific region. This database has been instrumental in developing the AARC score and grade of ACLF, the concept of the 'Golden Therapeutic Window', the 'transplant window', and plasmapheresis as a treatment modality. Also, the data has been key to identifying pediatric ACLF. The European Association for the Study of Liver-Chronic Liver Failure (EASL CLIF) and the North American Association for the Study of the End Stage Liver Disease (NACSELD) from the West added the concepts of organ failure and infection as precipitants for the development of ACLF and CLIF-Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) and NACSELD scores for prognostication. The Chinese Group on the Study of Severe Hepatitis B (COSSH) added COSSH-ACLF criteria to manage hepatitis b virus-ACLF with and without cirrhosis. The literature supports these definitions to be equally effective in their respective cohorts in identifying patients with high mortality. To overcome the differences and to develop a global consensus, APASL took the initiative and invited the global stakeholders, including opinion leaders from Asia, EASL and AASLD, and other researchers in the field of ACLF to identify the key issues and develop an evidence-based consensus document. The consensus document was presented in a hybrid format at the APASL annual meeting in Kyoto in March 2024. The 'Kyoto APASL Consensus' presented below carries the final recommendations along with the relevant background information and areas requiring future studies.
Keywords: AARC; ACLF; Acute decompensation (AD); Cirrhosis; Non-acute decompensation (NAD); Organ failure; Recompensation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Figures





References
-
- Moreau R, Jalan R, Gines P, Pavesi M, Angeli P, Cordoba J, et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure is a distinct syndrome that develops in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2013;144(1426–1437):1437.e1421–1429 - PubMed
-
- Mochida S, Nakayama N, Ido A, Inoue K, Genda T, Takikawa Y, et al. Proposed diagnostic criteria for acute-on-chronic liver failure in Japan. Hepatol Res. 2018;48:219–224 - PubMed
-
- Wu T, Li J, Shao L, Xin J, Jiang L, Zhou Q, et al. Development of diagnostic criteria and a prognostic score for hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure. Gut. 2018;67:2181–2191 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

