Predictive modeling of biodegradation pathways using transformer architectures
- PMID: 39962584
- PMCID: PMC11834682
- DOI: 10.1186/s13321-025-00969-7
Predictive modeling of biodegradation pathways using transformer architectures
Abstract
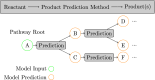
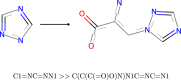
In recent years, the integration of machine learning techniques into chemical reaction product prediction has opened new avenues for understanding and predicting the behaviour of chemical substances. The necessity for such predictive methods stems from the growing regulatory and social awareness of the environmental consequences associated with the persistence and accumulation of chemical residues. Traditional biodegradation prediction methods rely on expert knowledge to perform predictions. However, creating this expert knowledge is becoming increasingly prohibitive due to the complexity and diversity of newer datasets, leaving existing methods unable to perform predictions on these datasets. We formulate the product prediction problem as a sequence-to-sequence generation task and take inspiration from natural language processing and other reaction prediction tasks. In doing so, we reduce the need for the expensive manual creation of expert-based rules.
Keywords: Biodegradation; Cheminformatics; Product prediction; Transfer-learning; Transformer.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: JSW is one of the founders of enviPath UG & Co. KG, a scientific software development company that develops and maintains enviPath. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- E Union (2020) Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 18 December 2006 concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH), establishing a European Chemicals Agency, amending Directive 1999/45/EC and repealing Council Regulation (EEC) No 793/93 and Commission Regulation (EC) No 1488/94 as well as Council Directive 76/769/EEC and Commission Directives 91/155/EEC, 93/67/EEC, 93/105/EC and 2000/21/EC (Text with EEA relevance) Text with EEA relevance. Legislative Body: OP_DATPRO. http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2006/1907/2020-08-24/eng. Accessed on 12 Mar 2024
-
- E Union (2012) Regulation (EU) No 528/2012 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 May 2012 concerning the making available on the market and use of biocidal products Text with EEA relevance. Legislative Body: CONSIL, EP. http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2012/528/oj/eng. Accessed 2 Dec 2024
-
- Wicker J, Fenner K, Ellis L, Wackett L, Kramer S (2010) Predicting biodegradation products and pathways: a hybrid knowledge- and machine learning-based approach. Bioinformatics 26(6):814–821. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq024 - PubMed
-
- Fenner K, Gao J, Kramer S, Ellis L, Wackett L (2008) Data-driven extraction of relative reasoning rules to limit combinatorial explosion in biodegradation pathway prediction. Bioinformatics 24(18):2079–2085. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn378 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

