Influence of Socio-Demographic, Occupational and Lifestyle Variables on Sleep Time
- PMID: 39963101
- PMCID: PMC11832214
- DOI: 10.2147/NSS.S495455
Influence of Socio-Demographic, Occupational and Lifestyle Variables on Sleep Time
Abstract
Background: Socio-demographic, occupational and lifestyle variables influence total sleep time. Therefore, we aimed to evaluate the influence of those variables on sleep time, and to study risk factors of being a short sleeper.
Methods: The COVISTRESS international study is an online questionnaire using the secure REDCap® software. Total sleep time was evaluated using declared bedtime and time of awakening and was analyzed as a quantitative variable and as a qualitative variable.
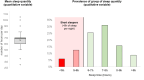
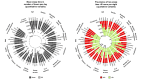
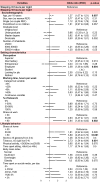
Results: We included 549 respondents to the questionnaire, divided into 10-year age groups ranging from <30yo to ≥60yo. The mean quantity of sleep was 7.11±1.43 hours per night. Factors that reduce total sleep time were age (coefficient -0.19, 95CI -0.33 to 0.06), being an employee (-0.46, -0.85 to -0.06), working time (-0.18, -0.31 to 0.05), smoking ≥5 cigarettes/day (-0.5, -0.95 to -0.20), high stress at work (-0.64, -0.96 to -0.32) and at home (-0.66, -0.97 to -0.35). Being a student (0.61, 0.02 to 1.19), working less than 25h per week (0.57, 0.17 to 0.97) and telework (0.46, 0.02 to 0.89) increased total sleep time. The risk factors of being a short sleeper were age (odds ratio 1.27, 95CI 1.07 to 1.51), being an employee (2.58, 1.36 to 4.89), smoking ≥5 cigarettes/day (2.73, 1.54 to 4.84) and a high level of stress at work (2.64, 1.45 to 4.82) and at home (3.89, 2.25 to 6.63). Physical activity ≥2.5 hours/week tended to decrease the risk of being a short sleeper by 35%.
Conclusion: We demonstrated the concomitant impact of sociodemographic, occupational and lifestyle behavior on sleep, which may help to build efficient preventive strategy.
Keywords: mental health; occupational variables; sociodemographic variables; total sleep time.
© 2025 Dutheil et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

