Identification of novel autoantibodies in Sjögren's disease
- PMID: 39963128
- PMCID: PMC11830686
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1524940
Identification of novel autoantibodies in Sjögren's disease
Abstract
Introduction: The diagnosis of Sjögren's disease (SjD) in patients without autoantibodies against Ro/SSA is a major challenge. We aimed to identify novel autoantibodies in SjD that may facilitate the diagnostic procedure for Ro/SSA negative SjD.
Methods: IgG and IgA autoantibody reactivity of 94 potential candidate autoantigens for SjD, selected from a discovery screen of 1,629 human antigens coupled to Luminex beads and prior knowledge about potential biological relevance, were examined in serum of SjD patients (n=347) using Luminex and ELISA technology. Healthy (HC, n=118) and non-Sjögren's sicca syndrome (NSS, n=44) individuals served as controls. To assess disease specificity, the novel autoantibodies were also measured in serum of patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA, n=50), Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE, n=49), and Systemic Sclerosis (SSc, n=37).
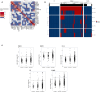
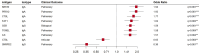
Results: 45 novel autoantibodies were significantly (p ≤ 0.05) more prevalent in SjD than in HC and were detected in up to 19% of the SjD cohort. The most common autoantibodies were against CCL4, M5, TMPO and OAS3. Some of the novel autoantibodies were associated with extraglandular disease manifestations, such as anti-TONSL or anti-IL6 with pulmonary involvement. We have developed a three and five marker panel for the detection of Ro/SSA negative patients, consisting of anti-FNBP4, anti-SNRPC, anti-CCL4, anti-M3 and anti-KDM6B, which had a sensitivity of up to 46% with a specificity of 95% (SjD vs. HC). Both panels discriminate these patients from HC, whereas the three-marker more effectively differentiates between Ro/SSA negative patients and NSS.
Discussion: Novel autoantibodies will facilitate the diagnosis of Ro/SSA negative patients with SjD, in particular our predictive panel will be useful in the diagnosis and differentiation of these patients from healthy and NSS individuals in a clinical context. In addition, the autoantibodies may also be useful for risk stratification of extraglandular manifestations.
Keywords: Sjögren’s disease; autoantibodies; biomarkers; connective tissue diseases; extraglandular manifestations; seronegative patients; sicca syndrome.
Copyright © 2025 Engelke, Budde, De Vita, Dörner, Ernst, Gras, Heidecke, Kilian, Kniesch, Lindemann, Quartuccio, Ritter, Schulze-Forster, Seeliger, Zucht and Witte.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors PB, ALK and H-DZ were employed by company Oncimmune Germany GmbH. Authors HH and KS-F were employed by company CellTrend GmbH. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer GV declared a past collaboration with the author LQ to the handling editor.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

