CAR-CIK vs. CAR-T: benchmarking novel cytokine-induced killer cells as solid tumor immunotherapy in ErbB2+ rhabdomyosarcoma
- PMID: 39963129
- PMCID: PMC11831232
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1485817
CAR-CIK vs. CAR-T: benchmarking novel cytokine-induced killer cells as solid tumor immunotherapy in ErbB2+ rhabdomyosarcoma
Abstract
Introduction: CAR-T cell therapy, though successful in hematologic malignancies, faces challenges in solid tumors due to limitations of autologous T cells. Cytokine-induced killer (CIK) cells can be given safely across allogeneic barriers and constitute alternative effector cells generated from healthy donors. CIK cells are a heterogenous population of predominantly T cells with a mixed natural killer (NK) phenotype and combine non-MHC-restricted cytotoxicity with potent anti-tumor capacity of the adaptive immune system. Here, we characterize and compare efficacy, phenotypic subpopulations and modes of action of CAR-CIK cells and conventional CAR-T cells from same-donor samples in ErbB2+ rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS).
Methods: To benchmark CAR-CIK against conventional CAR-T cells, effector cells were generated from same-donor samples and lentivirally transduced with a second generation CD28-CD3ζ CAR. Effector subpopulations and their dynamics upon target cell exposure were phenotypically characterized by flow cytometry. Efficacy was assessed in human ErbB2+ RMS cancer cell lines and primary patient samples in vitro and ex vivo using cytotoxicity and spheroid co-incubation assays. Modes of action were assessed by comparing cytokine secretion profiles using bead-based multiplexed flow cytometry and by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry whole cell proteomics. Finally, we used an in vivo model of RMS mimicking minimal metastatic residual disease to compare anti-tumor potency of CAR-CIK vs. CAR-T cells and to assess their target organ infiltration.
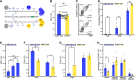
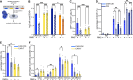
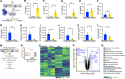
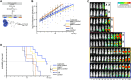
Results: In vitro assays demonstrated superior cytotoxicity of CAR-CIK cells against RMS cell lines and primary tumor samples. Long-term co-incubation with tumor spheroids led to expansion of CAR-CIK cells and enrichment of CD3+CD56+ TNK cells. CAR-CIK cell cytokine signature showed significantly increased secretion of effector molecules like interferon-γ, perforin and granulysin, and lower secretion of Th2 cytokines IL-2, IL-4 and IL-10. Whole cell proteomics showed corresponding upregulation of chemokine signaling and NK-cytotoxicity pathways in CAR-CIK cells. In NSG mice xenografted with ErbB2+ RMS, a single injection of either CAR-effector cells strongly impeded metastatic tumor development and significantly improved survival.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate that CAR-CIK cells are at least equipotent to CAR-T cells. Combined with their favorable safety profile and allogeneic applicability, these findings position CAR-CIK cells as promising immune effectors for solid tumors.
Keywords: CAR-T; ERBB2; cytokine-induced killer cells (CIK); rhabdomyosarcoma; solid tumors.
Copyright © 2025 Moser, Heim, Koschade, Wendel, Bozkurt, Harenkamp, Kreyenberg, Merker, Münch, Gradhand, Vogler, Ullrich, Bönig, Klusmann, Bader, Wels and Rettinger.
Conflict of interest statement
HB reports no conflicts of interest COI pertinent to the work at hand, but acknowledges research support from Bayer, Chugai, Erydel, Miltenyi, Polyphor, Sandoz-Hexal a Novartis company, Stage a Celgene company, Terumo BCT, and Uniqure; honoraria and speaker fees from Chugai, Fresenius, Genzyme, Kiadis, Medac, Miltenyi, Novartis, Sandoz-Hexal, and Terumo BCT; consultancy and membership in advisory boards for Apriligen, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Celgene a BMS company, Genzyme, Medac, NMDP, Novartis, Sandoz-Hexal, Stage, and Terumo BCT; royalties from Medac and stock ownership in Healthineers. J-HK declares to have no COI with regard to this manuscript, but acknowledges advisory roles for Bluebird Bio, Novartis, Roche and Jazz Pharmaceuticals. PB declares to have no COI with regard to the work at hand, but declares research grants from Neovii, Riemser, Medac, and BMS to institution; is a member of advisory boards for Novartis, Celgene, Amgen, Medac, Servier personal and institutional; has received speaker fees from Miltenyi, Jazz, Riemser, Novartis, and Amgen to institution; and declares a patent with and royalties from Medac. WW is named as an inventor on patents owned by Georg-Speyer-Haus that relate to ErbB2/HER2-specific CARs. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

References
-
- Myers RM, Jacoby E, Pulsipher MA, Pasquini MC, Grupp SA, Shah NN, et al. INSPIRED Symposium Part 1: Clinical Variables Associated with Improved Outcomes for Children and Young Adults treated with Chimeric Antigen Receptor T cells for B cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Transplant Cell Ther. (2023) 29:598–607. doi: 10.1016/j.jtct.2023.07.016 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

