Deferring Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Subacute STEMI With Rare Mechanical Complications
- PMID: 39963213
- PMCID: PMC11830274
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2024.103094
Deferring Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Subacute STEMI With Rare Mechanical Complications
Abstract
Background: Pseudoaneurysms and walls defects are rare mechanical complications of myocardial infarction, more common in subacute or late presentations.
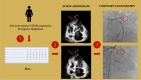
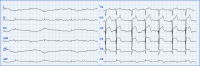
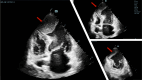
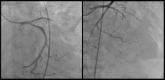
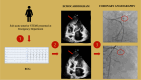
Case summary: A patient with subacute anterior ST elevation myocardial infarction presented to the emergency department with a large pseudoaneurysm of the apical septum, identified as an ischemic mechanical complication. Despite the confirmed complete occlusion of the left anterior descending artery, revascularization was deferred owing to the patient's high risk.
Discussion: The optimal timing for cardiac surgery in post-ischemic wall mechanical complications remains unclear. Evidence suggests immediate repair may prevent deterioration, while some surgeons recommend delaying surgery for 3 to 6 weeks to allow for fibrotic scar formation, aiding in safer suturing.
Take home message: This case highlights the importance of tailored patient management; the echocardiogram played a crucial role in identifying the optimal treatment strategy for this patient, balancing the risks of immediate intervention against the benefits of delayed surgery.
Keywords: heart rupture subacute; mechanical complications; pseudoaneurysm STEMI.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Bertolone is supported by a research grant from the CardioPaTh PhD Program. All other authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Subacute Left Ventricular Free Wall Rupture after Delayed STEMI Presentation During the COVID-19 Pandemic.JACC Case Rep. 2020 Aug;2(10):1603-1609. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2020.06.040. Epub 2020 Jul 8. JACC Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32835259 Free PMC article.
-
Concurrent acute myocardial infarction and acute ischemic stroke in a diabetic patient undergoing chemotherapy for non-Hodgkin lymphoma: Should I administer thrombolytic therapy? A case report.Egypt Heart J. 2024 Dec 25;76(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s43044-024-00593-0. Egypt Heart J. 2024. PMID: 39722069 Free PMC article.
-
A Rare Case of ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI) in a Paced Rhythm Meeting Full Sgarbossa Criteria in a 61-Year-Old Male With Complex Percutaneous Coronary Intervention and Post-Infarction Management Challenges.Cureus. 2025 Mar 7;17(3):e80192. doi: 10.7759/cureus.80192. eCollection 2025 Mar. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40190878 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous Left Ventricular Aneurysm and Ventricular Septal Rupture Complicating Delayed STEMI Presentation: A Case-Based Review of Post-MI Mechanical Complications Amid the COVID-19 Pandemic.J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2021 Jan-Dec;9:23247096211031135. doi: 10.1177/23247096211031135. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34259086 Free PMC article. Review.
-
API expert consensus document on management of ischemic heart disease.J Assoc Physicians India. 2006 Jun;54:469-80. J Assoc Physicians India. 2006. PMID: 16909697 Review.
References
-
- Byrne R.A., Rossello X., Coughlan J.J., et al. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes. Eur Heart J. 2023;44:3720–3826. - PubMed
-
- Schömig A., Mehilli J., Antoniucci D., et al. Mechanical reperfusion in patients with acute myocardial infarction presenting more than 12 hours from symptom onset: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2005;293:2865–2872. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

