tMCS Causing Myocardial Extramedullary Hematopoiesis Secondary to Massive Hemolysis
- PMID: 39963225
- PMCID: PMC11830249
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2024.103127
tMCS Causing Myocardial Extramedullary Hematopoiesis Secondary to Massive Hemolysis
Abstract
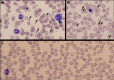
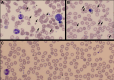
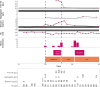
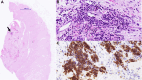
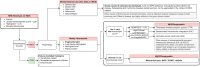
In severe heart failure with hemodynamic failure, when inotropic therapies no longer suffice (INTERMACS [Interagency Registry for Mechanically Assisted Circulatory Support] 1), temporary mechanical support is used as a bridging measure until a more definitive treatment, such as a left ventricular assist device, a total artificial heart or transplantation, is performed. Due to shear stress during the passage of blood through the pump, limited hemolysis is to be expected. We describe the case of a 37-year-old patient with terminal heart failure who suffered severe hemolysis during treatment with temporary mechanical support. Examination of the cardiac apex after left ventricular assist device implantation revealed a poorly differentiated tumor. Histopathologic examination revealed underlying extramedullary hematopoiesis, triggered by severe hemolytic anemia. Following exclusion of neoplasia, the patient subsequently underwent heart transplantation. Post-transplantation, the patient was diagnosed with alpha-thalassemia and heterozygote hemoglobin E. This combination can result in mild thalassemia with chronic low-level hemolysis and mild anemia, probably severely exacerbated in the presence of high-shear stress.
Keywords: acute heart failure; blood; cardiac assist devices; cardiac transplant; complication; dysplasia; imaging; treatment.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Esposito M.L., Morine K.J., Annamalai S.K., et al. Increased plasma-free hemoglobin levels identify hemolysis in patients with cardiogenic shock and a trans valvular micro-axial flow pump. Artif Organs. 2019;43(2):125–131. - PubMed
-
- Hill D.A., Swanson P.E. Myocardial extramedullary hematopoiesis: a clinicopathologic study. Mod Pathol. 2000;13(7):779–787. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

