Neuron with well-designed ionic system
- PMID: 39963598
- PMCID: PMC11830477
- DOI: 10.2142/biophysico.bppb-v21.0028
Neuron with well-designed ionic system
Abstract
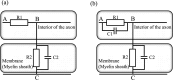
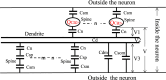
Neurons have an ionic system with several types of ion pumps and ion channels on their membranes. Each ion pump creates a specific difference in ion concentration inside and outside the neuron, and the energy resulting from this difference in concentration is maintained inside the neuron as a resting potential. Each ion channel senses the necessary situation, opens the channel, and allows the corresponding ion to pass through to perform its corresponding role. This ionic system realizes important functions such as (i) fast conduction of action potentials, (ii) achieving synaptic integration in response to several inputs with a time lag, and (iii) the information processing functions by neural circuits. However, the mechanisms by which these functions are realized have remained unclear. Therefore, based on the reports on various highly polymeric ion pumps, ion channels, cell membranes, and other components that have been elucidated so far, author analyzed how this ionic system can realize the above important functions from an electrical circuit designer point of view. As a result of a series of analyses, it was found that neurons realize each function by making full use of high-density packaging technology based on basic electrical principles and making maximum use of the extremely high dielectric properties of the ionic fluid of neurons. In other words, neuron looks to equip well designed ionic system which is the collaboration by designers of proteins and membranes that perform advanced functions and designers of electrical circuits that utilize them to achieve important functions electrically.
Keywords: capacitance; conduction velocity; dielectric constant; neural circuits; synaptic integration.
2024 THE BIOPHYSICAL SOCIETY OF JAPAN.
Conflict of interest statement
Author declares no conflicts of interest. Author declares no funding sources.
Figures
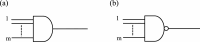



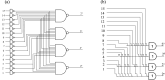
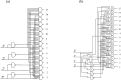
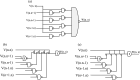
References
-
- Tsubo, T., Kurokawa, M.. Verification of the effect of the axon fluid as a highly dielectric medium in the high-speed conduction of action potentials using a novel axon equivalent circuit. Biophys. Physicobiol. 15, 214–228 (2018). https://doi.org/10.2142/biophysico.15.0_214 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tasaki, I. The electro-saltatory transmission of the nerve impulse and the effect of narcosis upon the nerve fiber. Am. J. Physiol. 127, 211–227 (1939). https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplegacy.1939.127.2.211
-
- Tsubo, T. Analysis of the mechanism of synaptic integration focusing on the charge held in the spine. Biophys. Physicobiol. 18, 290–304 (2021). https://doi.org/10.2142/biophysico.bppb-v18.036 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tsubo, T. Comparing neural and digital circuits on achieving basic functions necessary for data processing. European Journal of Biophysics 11, 25–39 (2023). https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ejb.20231102.11
-
- Hursh, J. B. Conduction velocity and diameter of nerve fibers. Am. J. Physiol. 127, 131–139 (1939). https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplegacy.1939.127.1.131
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

