Predicting Drug Resistance: The Use of Novel Inflammatory Markers in Identifying ESBL-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae
- PMID: 39963685
- PMCID: PMC11831217
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S506046
Predicting Drug Resistance: The Use of Novel Inflammatory Markers in Identifying ESBL-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae
Abstract
Purpose: To explore the association of the Systemic Inflammatory Response Index (SIRI) and Systemic Inflammatory Immunity Index (SII) with extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae (K. pneumoniae) and its resistance prediction.
Methods: A total of 425 patients with K. pneumoniae infections were included in the study. Data on general clinical characteristics and relevant laboratory indicators were collected. The patients were divided into ESBL-producing and non-ESBL-producing groups based on the presence of ESBLs. Logistic regression analysis was used to analyze the risk factors associated with ESBL-producing K. pneumoniae. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was employed to assess the predictive efficacy of SIRI and SII for ESBL-producing K. pneumoniae and its resistance to antibiotics.
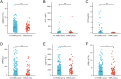
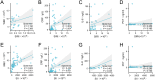
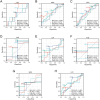
Results: SIRI and SII levels in the ESBL-producing group were significantly higher than those in the non-ESBL-producing group. Logistic regression analysis showed that the odds ratios for SIRI and SII were 1.092 and 1.158, respectively, with 95% confidence intervals of 1.001-1.115 and 1.015-1.204, respectively. The critical values for predicting ESBL-producing K. pneumoniae were 1.067 for SIRI and 579.68 for SII, with area under the curve (AUC) values of 0.725 and 0.723, respectively. The AUC values for predicting resistance of ESBL-producing K. pneumoniae to piperacillin (PIP), amoxicillin/clavulanate (AMC), and cefazolin (CZO) were 0.614, 0.657, and 0.648 for SIRI, and 0.675, 0.613, and 0.625 for SII, respectively.
Conclusion: SIRI and SII are significantly associated with the risk of ESBL-producing K. pneumoniae and can be used to predict a patient's risk of infection with this organism. Additionally, SIRI and SII accurately predict the resistance of ESBL-producing K. pneumoniae to PIP, AMC, and CZO antibiotics.
Keywords: Klebsiella pneumoniae; extended-spectrum β-lactamase; prediction of drug resistance; systemic inflammation response index; systemic inflammatory immune index.
© 2025 Ma et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Higher systemic immune-inflammation index and systemic inflammation response index levels are associated with stroke prevalence in the asthmatic population: a cross-sectional analysis of the NHANES 1999-2018.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 4;14:1191130. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1191130. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37600830 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization of Extended Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Clinical Isolates of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in Two Kenyan Facilities: A National Referral and a Level Five Hospital.Int J Microbiol. 2024 Feb 14;2024:7463899. doi: 10.1155/2024/7463899. eCollection 2024. Int J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38384586 Free PMC article.
-
SIRI and SII as potential biomarkers of disease activity and lupus nephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 31;16:1530534. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1530534. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39958362 Free PMC article.
-
Immune-inflammatory biomarkers for the occurrence of MACE in patients with myocardial infarction with non-obstructive coronary arteries.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 May 1;11:1367919. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1367919. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38751661 Free PMC article.
-
Usefulness of the Systemic Inflammation Response Index and the Systemic Immune Inflammation Index in Predicting Restenosis After Stent Implantation.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Jul 23;17:4941-4955. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S461277. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39051057 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashurst JV, Dawson A. Klebsiella Pneumonia. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023. - PubMed
-
- Hussein RA, Al-Kubaisy SH, Al-Ouqaili MTS. The influence of efflux pump, outer membrane permeability and β-lactamase production on the resistance profile of multi, extensively and pandrug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Infect Public Health. 2024;17(11):102544. doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2024.102544 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Coque TM, Oliver A, Pérez-Díaz JC, et al. Genes Encoding TEM-4, SHV-2, and CTX-M-10 extended-spectrum β-lactamases are carried by multiple Klebsiella pneumoniae clones in a single hospital (Madrid, 1989 to 2000). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002;46(2):500–510. doi:10.1128/AAC.46.2.500-510.2002 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chopra T, Marchaim D, Johnson PC, et al. Risk factors for bloodstream infection caused by extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae: a focus on antimicrobials including cefepime. Am J Infect Control. 2015;43(7):719–723. doi:10.1016/j.ajic.2015.02.030 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

