Effectiveness of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and molnupiravir on post-COVID-19 outcomes among outpatients: a target trial emulation investigation
- PMID: 39964106
- PMCID: PMC11881657
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2025.2469648
Effectiveness of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and molnupiravir on post-COVID-19 outcomes among outpatients: a target trial emulation investigation
Abstract
Limited studies compared the effectiveness of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and molnupiravir against a control group on post-COVID-19 conditions. Our study examined the association of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and molnupiravir with post-acute mortality and hospitalizations among outpatients using real-world outpatient records of COVID-19 designated clinics in Hong Kong. This is an observational study using a target trial emulation framework, involving nirmatrelvir-ritonavir versus no antiviral treatment (Trial 1) and molnupiravir versus no antiviral treatment (Trial 2). Outcomes included post-acute mortality, all-cause hospitalization, and hospitalization due to 13 selected sequelae. Relative effectiveness was assessed by comparing the cumulative incidence between two groups, reported as relative risk (RR), along with risk differences (RD) during day 0-30, 31-180, and 181-360. After screening, 140,477 and 96,030 patients were included in Trial 1 and 2, respectively. Compared with no treatment, nirmatrelvir/ritonavir-treated patients exhibited a significantly lower risk of post-acute mortality (31-180 days: RR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.54-0.96; RD, 0.20%; 181-360 days: RR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.50-0.82; RD, 0.32%) and all-cause hospitalization (31-180 days: RR, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.76-0.88; RD, 1.11%; 181-360 days: RR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.78-0.89; RD, 1.18%). Patients receiving molnupiravir had a lower risk of 30-day mortality, but no significant beneficial effect was observed for the post-acute outcomes. In conclusion, this study demonstrated the effectiveness of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in reducing post-COVID-19 outcomes among outpatients. While we observed the short-term effectiveness of molnupiravir in reducing mortality, no protective effect on long-term post-COVID-19 outcomes was observed.
Keywords: Post-COVID-19 outcomes; molnupiravir; nirmatrelvir/ritonavir; target trial emulation.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
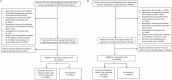
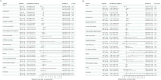
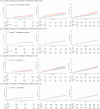
References
-
- Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for Paxlovid™. Available from: www.fda.gov/media/155050/download
-
- Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for Lagevrio™ (molnupiravir) capsules. Available from: www.fda.gov/media/155054/download
-
- Wong CKH, Au ICH, Lau KTK, et al. . Real-world effectiveness of early molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 without supplemental oxygen requirement on admission during Hong Kong's omicron BA.2 wave: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2022;22 (12):1681–1693. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
