Noninvasive Monitoring of Palmitoyl Hexapeptide-12 in Human Skin Layers: Mechanical Interaction with Skin Components and Its Potential Skincare Benefits
- PMID: 39964201
- PMCID: PMC11920943
- DOI: 10.1021/acsabm.4c01816
Noninvasive Monitoring of Palmitoyl Hexapeptide-12 in Human Skin Layers: Mechanical Interaction with Skin Components and Its Potential Skincare Benefits
Abstract
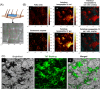
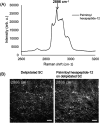
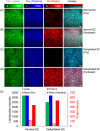
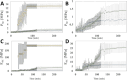
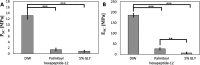
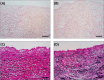
Self-assembling peptides (SAPs) represent a rich source of building blocks that interact with biological structures. For instance, cosmetic SAPs like Palmitoyl hexapeptide-12 have gained increasing interest for their anti-aging properties. However, their short-term impact on the skin composition and mechanics remains unclear. In this study, a battery of label-free techniques is exploited to objectively monitor the effects of Palmitoyl hexapeptide-12 on human skin. Orbital trapping secondary ion mass spectrometry (OrbiSIMS) is used to discern between Palmitoyl hexapeptide-12 sol and gel forms, tracking its self-assembly and penetration within full-thickness human skin. Palmitoyl hexapeptide-12 is shown to permeate both stratum corneum and epidermal layers, initiating gel formation by harnessing endogenous ions. Hence, the ability of the peptide to strengthen and repair the skin barrier after delipidation is also demonstrated through a high-throughput mechanical characterization and stimulated Raman scattering (SRS). Finally, the co-assembling properties of Palmitoyl hexapeptide-12 with native skin molecules are shown via in vitro tests and ex vivo histology. This study establishes a methodological benchmark for measuring the effects of cosmetic peptides on skin mechanics and hydration, introducing a platform to design SAPs capable of harnessing native skin molecules to create "biocooperative" structures with cosmetic benefits.
Keywords: OrbiSIMS; Palmitoyl hexapeptide-12; SRS; cosmetics; human skin; self-assembling peptides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Cai H.; Wu F.-Y.; Wang Q.-L.; Xu P.; Mou F.-F.; Shao S.-J.; Luo Z.-R.; Zhu J.; Xuan S.-S.; Lu R.; Guo H.-D. Self-Assembling Peptide Modified with QHREDGS as a Novel Delivery System for Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation after Myocardial Infarction. FASEB J. 2019, 33 (7), 8306–8320. 10.1096/fj.201801768RR. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lindsey S.; Piatt J. H.; Worthington P.; Sönmez C.; Satheye S.; Schneider J. P.; Pochan D. J.; Langhans S. A. Beta Hairpin Peptide Hydrogels as an Injectable Solid Vehicle for Neurotrophic Growth Factor Delivery. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16 (9), 2672–2683. 10.1021/acs.biomac.5b00541. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
