The Crosstalk with CXCL10-Rich Tumor-Associated Mast Cells Fuels Pancreatic Cancer Progression and Immune Escape
- PMID: 39965084
- PMCID: PMC11984875
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202417724
The Crosstalk with CXCL10-Rich Tumor-Associated Mast Cells Fuels Pancreatic Cancer Progression and Immune Escape
Abstract
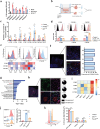
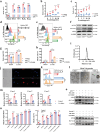
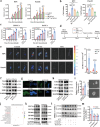
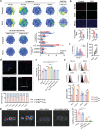
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a devastating disease, necessitating approaches to improve prognosis. As the mediator of allergic process, mast cells have been found in various cancers and are associated with survival. However, the biological behaviors of tumor-associated mast cells (TAMCs) remain unclear. Herein, an excessive infiltration of TAMCs in PDAC is demonstrated, which apparently associated with poor survival in PDAC patients. PDAC cells are found to recruit CXCR2+ MCs into TME, and then inhibited MCs ferroptosis, and maintained their proliferation. Concomitantly, the tumor-derived exosome miR-188-5p activated the PTEN/AKT/GSK3β signaling, further stabilized transcriptional factor ERG by inhibiting its ubiquitin degradation, and finally enhanced the transcription of cxcl10 within TAMCs. In reverse, TAMCs-derived CXCL10 reversely promoted tumor epithelial-mesenchymal transition and induced immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment by recruiting CXCR3+ Tregs. Sodium cromoglycate (SCG) is a membrane stabilizer for MCs and confirmed as an effective and widely used agent to block TAMCs-derived CXCL10 and further sensitize the therapeutic efficacy of anti-PD-1 antibody plus gemcitabine for PDAC. These findings illuminate a critical and innovative crosstalk between TAMCs and PDAC cells that promote PDAC progression, and SCG sensitizes PDAC to the current immuno-chemotherapy, which reveals its potential to be a valuable adjuvant for PDAC patients.
Keywords: CXCL10; immune escape; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; sodium cromoglycate; tumor‐associated mast cell.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82103409/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82202969/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82273382/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82272929/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82473459/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- Y-Gilead2024-PT-0002/Beijing CSCO-Clinical Oncology Research Foundation
- Y-HR2022MS-0251/Beijing CSCO-Clinical Oncology Research Foundation
- Y-2022METAZQN-0003/Beijing CSCO-Clinical Oncology Research Foundation
- 20244Y0023/Shanghai Municipal Health Commission
- 21YF1407100/Shanghai "Rising Stars of Medical Talents" Youth Development Program, Shanghai Sailing Program
- 2021M690037/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- FMUGIC-202301/Open Research Fund of Key Laboratory of Gastrointestinal Cancer (Fujian Medical University), Ministry of Education
- TCM2024-2/Fund of Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Translational Cancer Medicine
- 23XD1400600/Program of Shanghai Academic/Technology Research Leader
- 24SF1900300/Shanghai Science and Technology Commission Innovative Pharmaceutical Products Application Demonstration Project
- 202305AF150148/Science and Technology Planning Project of Yunnan Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
