Bioturbation in the hadal zone
- PMID: 39966393
- PMCID: PMC11836284
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-56627-x
Bioturbation in the hadal zone
Abstract
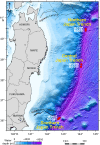
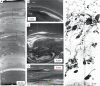
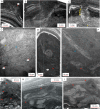
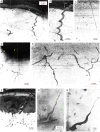
The hadal zone, >6 km deep, remains one of the least understood ecosystems on Earth. We address bioturbational structures in sediment cores from depths exceeding 7.5 km, collected during the IODP Expedition 386 in the Japan Trench. Micro-CT imaging on 20 core sections allowed to identify biogenic sedimentary structures (incipient trace fossils) and their colonization successions within gravity flow deposits. Their frequency, and consequent changes in substrate consistency, oxygenation and organic matter delivery and remineralization controlled the endobenthic colonization. The gravity-flow beds show recurring bioturbation successions: The initial colonization is characterized by deposit-feeding structures such as Phycosiphon, Nereites and Artichnus generating typically 20 cm thick intensively bioturbated fabrics. The final colonization stage comprises slender spiral, lobate and deeply penetrating straight and ramifying burrow systems such as Gyrolithes, Pilichnus and Trichichnus, interpreted to include burrows of microbe farming and chemosymbiotic invertebrates. The main factor precluding colonization is soupy substrate. Organic matter degradation and post-event upward expansion of the anoxic zone drive the change from deposit feeding to microbe-dependent feeding strategies.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Jamieson, A. The Hadal Zone: Life in the Deepest Oceans. (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 2015).
-
- Kioka, A. & Strasser, M. Oceanic Trenches. in Treatise on Geomorphology (Second Edition) (ed. Shroder, J. (Jack) F.) vol. 8 882–900 (Academic Press, Oxford, 2022).
-
- Hughes, D. J. & Gage, J. D. Benthic metazoan biomass, community structure and bioturbation at three contrasting deep-water sites on the northwest European continental margin. Prog. Oceanogr.63, 29–55 (2004).
-
- Jamieson, A. J., Fujii, T., Mayor, D. J., Solan, M. & Priede, I. G. Hadal trenches: the ecology of the deepest places on Earth. Trends Ecol. Evol.25, 190–197 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Stewart, H. A. & Jamieson, A. J. Habitat heterogeneity of hadal trenches: Considerations and implications for future studies. Prog. Oceanogr.161, 47–65 (2018).
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

