Accelerating veterinary low field MRI acquisitions using the deep learning based denoising solution HawkAI
- PMID: 39966480
- PMCID: PMC11836044
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-88822-7
Accelerating veterinary low field MRI acquisitions using the deep learning based denoising solution HawkAI
Abstract
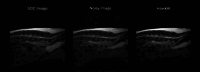
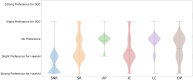
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has changed veterinary diagnosis but its long-sequence time can be problematic, especially because animals need to be sedated during the exam. Unfortunately, shorter scan times implies a fall in overall image quality and diagnosis reliability. Therefore, we developed a Generative Adversarial Net-based denoising algorithm called HawkAI. In this study, a Standard-Of-Care (SOC) MRI-sequence and then a faster sequence were acquired and HawkAI was applied to the latter. Radiologists were then asked to qualitatively evaluate the two proposed images based on different factors using a Likert scale (from 1 being strong preference for HawkAI to 5 being strong preference for SOC). The aim was to prove that they had at least no preference between the two sequences in terms of Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) and diagnosis. They slightly preferred HawkAI in terms of SNR (confidence interval (CI) being [1.924-2.176]), had no preference in terms of Artifacts Presence, Diagnosis Pertinence and Lesion Conspicuity (respective CIs of [2.933-3.113], [2.808-3.132] and [2.941-3.119]), and a very slight preference for SOC in terms of Spatial Resolution and Image Contrast (respective CIs of [3.153-3.453] and [3.072-3.348]). This shows the possibility to acquire images twice as fast without any major drawback compared to a longer acquisition.
Keywords: MRI; Machine learning; Veterinary imaging.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: J.N. and M.B. are employees of HawkCell. V.C. was an employee of Hawkcell at the time of this research. H.D. is the founder and Chief Scientific Officer of HawkCell and owns stock in the company.
Figures




References
-
- Gavin, P. Growth of clinical veterinary magnetic resonance imaging. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound52, S2–S4. 10.1111/j.1740-8261.2010.01779.x (2011). - PubMed
-
- Thomson, C. E. et al. Magnetic resonance imaging’a general overview of principles and examples in veterinary neurodiagnosis. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound34, 2–17. 10.1111/j.1740-8261.1993.tb01986.x (1993).
-
- Werpy, N. M. Magnetic resonance imaging of the equine patient: A comparison of high-and low-field systems. Clin. Tech. Equine Pract.6, 37–45. 10.1053/j.ctep.2006.11.004 (2007).
-
- Redpath, T. W. Signal-to-noise ratio in mri. Br. J. Radiol.71, 704–707. 10.1259/bjr.71.847.9771379 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Rudin, L. I. Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms. Physica D60, 259–268. 10.1016/0167-2789(92)90242-F (1992).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

