Systemic inflammation response index predicts overall survival in patients undergoing stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastasis from non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 39967449
- PMCID: PMC11932349
- DOI: 10.1093/jrr/rrae099
Systemic inflammation response index predicts overall survival in patients undergoing stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastasis from non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
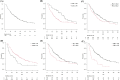
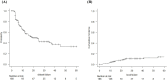
This study aimed to evaluate the prognostic value of pre-treatment blood cell counts in patients with brain metastasis (BM) from non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who were treated using linear accelerator (linac)-based stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) and fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (fSRT) with a micro-multileaf collimator. Between January 2011 and November 2022, 271 consecutive patients underwent linac-based SRS/fSRT for BM from NSCLC. Thirty patients with insufficient blood test data during this period were excluded from this analysis. Thirty-five patients with steroid intake at the time point of the blood test and 18 patients with higher C-reactive protein were excluded. Thus, 188 patients were eventually enrolled in this study. The median follow-up period after SRS/fSRT was 21 months (range: 0-121 months), and the median survival time after SRS/fSRT was 19 months. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio ≥ 1.90, lymphocyte-monocyte ratio ≤ 1.67 and systemic inflammation response index (SIRI) ≥ 2.95 were unfavorable predictors of prognosis for patients who underwent SRS/fSRT for BM from NSCLC. Cox proportional-hazard multivariate analysis revealed that the SIRI was independent prognostic factors for increased risk of death. Thus, simple, less expensive, and routinely performed pre-treatment blood cell count measurements such as SIRI can predict the overall survival of patients treated with SRS/fSRT for BM from NSCLC.
Keywords: brain metastasis; neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio; non-small cell lung cancer; systemic immune-inflammation index; systemic inflammation response index.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Japanese Radiation Research Society and Japanese Society for Radiation Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Upfront Stereotactic Radiosurgery or Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy in Elderly Patients with Brain Metastases from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Analysis of a 10-Year Bi-institutional Experience.Cancer Res Treat. 2025 Jan;57(1):47-56. doi: 10.4143/crt.2024.223. Epub 2024 Jul 3. Cancer Res Treat. 2025. PMID: 38965923 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Results and Hematologic Predictors of Linear Accelerator-Based Stereotactic Radiosurgery or Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Brain Metastasis in Patients Aged 75 Years or Older: A Retrospective Study.World Neurosurg. 2024 Mar;183:e944-e952. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2024.01.069. Epub 2024 Jan 19. World Neurosurg. 2024. PMID: 38244685
-
Long-Term Survival after Linac-Based Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Radiotherapy with a Micro-Multileaf Collimator for Brain Metastasis.Curr Oncol. 2022 Aug 24;29(9):6068-6076. doi: 10.3390/curroncol29090477. Curr Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36135046 Free PMC article.
-
Stereotactic radiosurgery versus stereotactic radiotherapy in the management of intracranial meningiomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Neurosurg Focus. 2019 Jun 1;46(6):E2. doi: 10.3171/2019.3.FOCUS1970. Neurosurg Focus. 2019. PMID: 31153149
-
Surgery of enlarging lesions after stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases in patients with non-small cell lung cancer with oncogenic driver mutations frequently reveals radiation necrosis: case series and review.APMIS. 2024 Jun;132(6):375-381. doi: 10.1111/apm.13402. Epub 2024 Mar 11. APMIS. 2024. PMID: 38466886 Review.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

