Making stereopsis related to the ability of ocular deviation: a new paradigm for assessment of intermittent exotropia
- PMID: 39967967
- PMCID: PMC11754039
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2025.02.15
Making stereopsis related to the ability of ocular deviation: a new paradigm for assessment of intermittent exotropia
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the underlying factors by establishing a new paradigm for assessing control ability under stereopsis testing conditions.
Methods: This was a prospective observational study. We evaluated the control ability of intermittent exotropia (IXT) patients in three conditions: natural 2D optotype viewing, 2D optotype viewing with polarized glasses, and 3D optotype viewing with polarized glasses. Recording with a smartphone, we captured videos to analyze the accurate time of spontaneous exodeviation and subsequent realignment before and after breaking fusion. Additionally, the correlation of stereopsis were also analyzed.
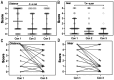
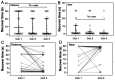
Results: A total of 48 patients (age range: 4-33y; 54.17% male) participated in the study. When viewing 3D optotypes with polarized glasses, their median control scores were 1 (interquartile range, 0-4) at distance and 0 (0-1) at near. These scores were significantly better than those observed under natural viewing conditions, which were 2.5 (1-5) at a distance and 1 (0-3) at near (Friedman test, P=0.049). Furthermore, those subjects who exhibited exophoria (realignment within 2 seconds) while viewing 3D optotypes with polarized glasses were more likely to have measurable stereo vision (Kendall's τb=-0.344, P=0.018).
Conclusion: IXT patients exhibit enhanced control ability when using polarized glasses to view 3D optotypes, notably improving realignment capabilities. This expands our understanding of current tests and offers a potentially sensitive method for assessing IXT severity.
Keywords: control ability; intermittent exotropia; stereopsis.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Li JB, None; Kong WT, None; Shen T, None; Yuan YG, None; Chen CL, None; Peng DM, None; Liang MT, None; He X, None; Luo D, None; Su JY, None; Wang W, None; Wang RX, None; Yu XP, None.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
