Folate-Functionalized CS/rGO/NiO Nanocomposites as a Multifunctional Drug Carrier with Anti-Microbial, Target-Specific, and Stimuli-Responsive Capacities
- PMID: 39968060
- PMCID: PMC11834734
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S489418
Folate-Functionalized CS/rGO/NiO Nanocomposites as a Multifunctional Drug Carrier with Anti-Microbial, Target-Specific, and Stimuli-Responsive Capacities
Abstract
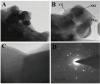
Purpose: This study reports the synthesis of surface-modified chitosan (CS) coated with reduced graphene oxide/nickel oxide (rGO/NiO) as a multifunctional drug carrier with anti-microbial, target-specific, and stimuli-responsive capacities. CS, rGO, and NiO nanoparticles are selected due to their pH-responsiveness, large surface area, and ROS generating-capacity, respectively.
Methods: The CS/rGO/NiO nanocomposites (NCs) are synthesized using a solvothermal approach. Glutaraldehyde is used to crosslink CS and rGO/NiO to enhance the stability of the NCs. Structural properties, magnetic properties, antimicrobial activity, drug release sustainability and toxicity of the NCs are evaluated.
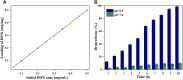
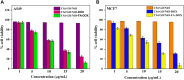
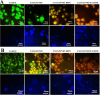
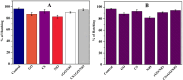
Results: The NCs show good biocompatibility, excellent magnetic properties, good target specificity, and remarkable cell growth inhibitory effects. The release of doxorubicin (DOX) from the drug-loaded NCs at pH 5.0 (~98.6%) is much higher than that at pH 7.4 (~9.6%). Furthermore, the NCs inhibit the growth of A549 and MCF7 cells, causing the viability of A549 and MCF7 to drop to 12.3% and 7.1%, respectively. By using zebrafish embryos as a model, no detectable change is observed in the survival rate of the embryos after NC treatment.
Conclusion: The NCs exhibit multifunctional, target-specific, and pH-responsive characteristics. These properties make the NCs a promising candidate for use in drug delivery applications.
Keywords: biopolymer; drug delivery; folate receptor; nanoparticles; nickel oxide.
© 2025 Obireddy et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures









References
-
- Lv Y-C, Esmaeili Shahri E, Mahmoudi A, Keifi Naughabi R, Abbaspour S, Tayebee R. Bioinspired nickel oxide nanoparticle as an efficient nanocarrier in the delivery of doxorubicin as an anti-bladder cancer drug. Inorg Chem Commun. 2023;152:110650. doi:10.1016/j.inoche.2023.110650 - DOI
-
- Punitha U, Mary Saral A. Nickel oxide nanoparticles from Sargassumwightii: synthesis, Characterization, and biomedical applications. Results Chem. 2024;7:101289. doi:10.1016/j.rechem.2023.101289 - DOI
-
- AlSalhi MS, Aziz MH, Atif M, et al. Synthesis of NiO nanoparticles and their evaluation for photodynamic therapy against HeLa cancer cells. J King Saud Univ Sci. 2020;32(2):1395–1402. doi:10.1016/j.jksus.2019.11.033 - DOI
-
- Aarthi J, Kaviya SS, Kirubavathi K, et al. Green synthesis of nickel oxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of Mimosa pudica for killing triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and bacteria. J Mol Struct. 2025;1321:140178. doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2024.140178 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

