Effects of Melissa officinalis Extracts on Obesity and Anxiety
- PMID: 39968272
- PMCID: PMC11832291
- DOI: 10.7762/cnr.2025.14.1.65
Effects of Melissa officinalis Extracts on Obesity and Anxiety
Abstract
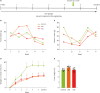
Obesity is a significant global health concern that not only increases metabolic disorders risks but also impacts mental health, particularly affecting women due to hormonal fluctuations and societal pressures. This study investigated anti-obesity and anti-anxiety effects of lemon balm (Melissa officinalis) extracts in female C57BL/6 mouse (n = 16, 17 weeks old) fed a high-fat diet (HFD). We compared 2 extracts method: distilled water (LBD, n = 5) and 80% ethanol (LBE, n = 6), administered via oral gavage (200 mg/kg/day) for 6 weeks alongside HFD. Both extract groups showed lower weight increase ratio compared to the control group in experiment period (n = 5) (LBD: 27.74%, LBE: 29.71% vs. Control: 51.88%, p < 0.05). The extracts significantly decreased mesenteric white adipose tissue (mWAT) among WATs examined (mWAT and parametrial white adipose tissue [pWAT]). While both LBD and LBE reduced fatty acid synthase (FAS) mRNA expression in pWAT, only LBD reduced peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and FAS mRNA expression in mWAT. In elevated plus maze behavioral experiments, the LBD group displayed reduced anxiety-like behavior, spending significantly more time and travelling greater distances in the open arms compared to other groups (p < 0.05), independent of brain inflammatory markers. Our findings demonstrate lemon balm extracts simultaneously address both obesity and anxiety-like behaviors in female mice, with extraction solvent-dependent variations in efficacy and mechanism of action. These results suggest potential therapeutic applications for lemon balm as a functional food ingredient, particularly for women experiencing concurrent obesity and anxiety symptoms.
Keywords: Anxiety; Extraction solvent; Female; Lemon balm; Melissa officinalis; Obesity.
Copyright © 2025. The Korean Society of Clinical Nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The author declares that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Consultation on Obesity. Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic: report of a WHO consultation. Geneva: WHO; 2000. - PubMed
-
- Korean Society for the Study of Obesity. Obesity fact sheet. Seoul: Korean Society for the Study of Obesity; 2023.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

