Analysis of TTN Truncating Variants in >74 000 Cases Reveals New Clinically Relevant Gene Regions
- PMID: 39968638
- PMCID: PMC11999099
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCGEN.124.004982
Analysis of TTN Truncating Variants in >74 000 Cases Reveals New Clinically Relevant Gene Regions
Abstract
Background: Truncating variants (TTNtvs) in the titin (TTN) gene have been associated with cardiomyopathies or arrhythmias (C/A) and autosomal recessive neuromuscular diseases (NM). However, the clinical significance of TTNtvs across the entire coding sequence of TTN has not been comprehensively assessed. The purpose of this study was to examine the burden of TTNtvs in C/A and NM cases compared with controls in the genome aggregation database.
Methods: This was a retrospective study of probands who underwent multigene testing (49 740 C/A panel, 24 514 NM panel) that included TTN from November 2017 to October 2021. Burden testing was performed using controls in the genome aggregation database v3.1.2 database, and the analysis was stratified by exon/band location and exon usage in cardiac or skeletal muscle. Frequency and odds ratio of TTNtv alleles in C/A or NM cases and genome aggregation database controls were measured.
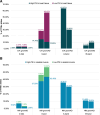
Results: There were 2446 (4.9%) C/A and 482 (2.0%) NM cases with 2446 and 528 TTNtv alleles, respectively. TTNtvs in all bands were significantly enriched in both C/A and NM cases compared with controls. A significant enrichment of TTNtvs in C/A was observed for exon 358 of the M-band (odds ratio, 2.55 [95% CI, 1.85-3.54]) but not the other M-band exons.
Conclusions: In the largest single-site cohort of C/A and NM cases with TTNtvs, an enrichment of TTNtvs across TTN was observed. These findings expand the clinically relevant regions of TTN.
Keywords: alleles; arrhythmias, cardiac; cardiomyopathies; exons; neuromuscular diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors are current employees of Labcorp (formerly Invitae Corporation) and former employees and shareholders of Invitae Corp. Invitae provided salary support for this project.
Figures
References
-
- Bang ML, Centner T, Fornoff F, Geach AJ, Gotthardt M, McNabb M, Witt CC, Labeit D, Gregorio CC, Granzier H, et al. . The complete gene sequence of titin, expression of an unusual approximately 700-kDa titin isoform, and its interaction with obscurin identify a novel Z-line to I-band linking system. Circ Res. 2001;89:1065–1072. doi: 10.1161/hh2301.100981 - PubMed
-
- Cardiovascular Genetics and Genomics Group. TTN transcript & exon structure. Titin variants in dilated cardiomyopathy. Accessed September 2022. https://www.cardiodb.org/titin/titin_transcripts.php
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

