Toward a New Conceptual Framework for Digital Mental Health Technologies: Scoping Review
- PMID: 39969824
- PMCID: PMC11864090
- DOI: 10.2196/63484
Toward a New Conceptual Framework for Digital Mental Health Technologies: Scoping Review
Abstract
Background: Digital mental health technologies (DMHTs) are becoming more widely available and are seen as having the potential to improve the quality of mental health care. However, conversations around the potential impact of DMHTs can be impacted by a lack of focus on the types of technologies that are available. Several frameworks that could apply to DMHTs are available, but they have not been developed with comprehensive methods and have limitations.
Objective: To address limitations with current frameworks, we aimed to identify existing literature on the categorization of DMHTs, to explore challenges with categorizing DMHTs for specific purposes, and to develop a new conceptual framework.
Methods: We used an iterative approach to develop the framework. First, we completed a rapid review of the literature to identify studies that provided domains that could be used to categorize DMHTs. Second, findings from this review and associated issues were discussed by an expert working group, including professionals from a wide range of relevant settings. Third, we synthesized findings to develop a new conceptual framework.
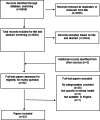
Results: The rapid review identified 3603 unique results, and hand searching identified another 3 potentially relevant papers. Of these, 24 papers were eligible for inclusion, which provided 10 domains to categorize DMHTs. The expert working group proposed a broad framework and based on the findings of the review and group discussions, we developed a new conceptual framework with 8 domains that represent important characteristics of DMHTs. These 8 domains are population, setting, platform or system, purpose, type of approach, human interaction, human responsiveness, and functionality.
Conclusions: This conceptual framework provides a structure for various stakeholders to define the key characteristics of DMHTs. It has been developed with more comprehensive methods than previous attempts with similar aims. The framework can facilitate communication within the field and could undergo further iteration to ensure it is appropriate for specific purposes.
Keywords: categorization; conceptual; digital health; digital mental health; eHealth; framework; mental health; regulation; review methodology; review methods; synthesis; systematic.
© Gareth Hopkin, Holly Coole, Francesca Edelmann, Lynda Ayiku, Richard Branson, Paul Campbell, Sophie Cooper, Mark Salmon. Originally published in JMIR Mental Health (https://mental.jmir.org).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Medicines & Healthcare products Regulatory Agency Crafting an intended purpose in the context of software as a medical device (SaMD) GOV.UK. 2023. [21-06-2024]. https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/crafting-an-intended-purpose-... URL. Accessed.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical