Curcumin's protective role against fluoride-induced bone damage: Implications for pullet pathology and skeletal biomechanics
- PMID: 39970518
- PMCID: PMC11879666
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.104891
Curcumin's protective role against fluoride-induced bone damage: Implications for pullet pathology and skeletal biomechanics
Abstract
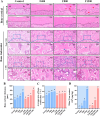
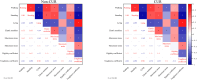
This study aimed to investigate the effects of dietary fluoride (F) and curcumin (Cur) supplementation on the tibial biomechanical performance, histopathology, and behavior of pullets. Four dietary F levels (0, 400, 800, 1200 mg/kg) supplemented with CUR (0, 200 mg/kg) were used to create 8 experimental groups in Hyline Brown pullets. Behavioral study results showed that supplements of 1200 mg/kg F reduced the percentages of feeding, walking, standing, and preening behaviors while increasing the percentage of lying behavior (P < 0.05). This is associated with F-induced tibial elastic modulus, maximum stress, and stiffness coefficient were reduced and toughness coefficient was increased (P < 0.05). F-induced tibial cortical bone thickened, trabecular bone widened, and excessive accumulation of bone collagen fibers (P < 0.05) in the tibia explained the biomechanical properties reduction in Hyline Brown pullets. Additionally, the loss of antioxidant capacity was mediated by excessive F-accelerated pathological damage to the bone (P < 0.05). Supplementation with 200 mg/kg CUR alleviated abnormal behavior, expansion of the trabecular bone, accumulation of collagen fibers, and loss of antioxidant capacity (P < 0.05). In conclusion, F reduced the antioxidant level of the body, caused tibia histopathological damage, destroyed the tibia biomechanical properties, and caused abnormal behavior of pullets. Supplementation with 200 mg/kg CUR attenuates F-induced oxidative and tibia damage and rectifies abnormal behavioral traits.
Keywords: Antioxidants; Behavior; Histopathology; Skeletal biomechanics; Skeletal fluorosis.
Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Ashry A.M., Hassan A.M., Habiba M.M., El-Zayat A., El-Sharnouby M.E., Sewilam H., Dawood M.A.O. The impact of dietary curcumin on the growth performance, intestinal antibacterial capacity and Haemato-biochemical parameters of Gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) Animals. 2021;11:1779. (Basel) - PMC - PubMed
-
- Del Razo L.M., Corona J.C., García-Vargas G., Albores A., Cebrián M.E. Fluoride levels in well-water from a chronic arsenicism area of Northern Mexico. Environ. Pollut. 1993;80:91–94. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

