The association of serum hsa-miR-21-5p expression with the severity and prognosis of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction
- PMID: 39972425
- PMCID: PMC11837298
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-024-04465-y
The association of serum hsa-miR-21-5p expression with the severity and prognosis of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction
Abstract
Background: Heart failure poses a huge burden on the global population, and approximately 50% cases have reduced ejection fraction, namely, heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). The research was supposed to explore the relationship between serum hsa-miR-21-5p expression and the severity/prognosis of HFrEF.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on 105 HFrEF patients and 86 healthy volunteers. RT-qPCR was used for the detection of serum hsa-miR-21-5p levels. Whether serum hsa-miR-21-5p expression correlated to cardiac function and hemodynamic indicators was evaluated using Spearman correlation analysis. Receiver operating characteristic and Kaplan-Meier analyses were implemented to evaluate the predictive significance of serum hsa-miR-21-5p for cardiovascular re-hospitalization and cardiovascular deaths in HFrEF patients. Independent risk factors for cardiovascular deaths were analyzed based on COX regression.
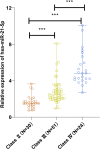
Results: Higher heart rate, fasting plasma glucose (FPG), N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-pro-BNP), left atrial diameter (LAD), systolic pulmonary artery pressure (sPAP), pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR), pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP), and hsa-miR-21-5p as well as lower left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and left ventricular fractional shortening (LVFS) were detected in the HFrEF patients than in the controls. Hsa-miR-21-5p expression increased in HFrEF patients with the increase of NYHA grade. Serum hsa-miR-21-5p expression in HFrEF patients was positively relevant to NT-pro-BNP, LAD, sPAP, PVR, and PCWP but negatively related to LVEF and LVFS. Serum hsa-miR-21-5p had a high predictive value for cardiovascular re-hospitalization and cardiovascular deaths in HFrEF patients. High hsa-miR-21-5p expression was an independent dangerous factor for cardiovascular deaths.
Conclusion: Collectively, hsa-miR-21-5p expression in HFrEF patients is correlated with disease severity and the risk of cardiovascular re-hospitalization and cardiovascular deaths in HFrEF patients, indicating a new direction for evaluating the disease situation and prognosis.
Keywords: Cardiac function; Cardiovascular deaths; Cardiovascular re-hospitalization; Disease severity; Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction; Hsa-miR-21-5p; NYHA grade; Prognosis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study followed the ethical guidelines of the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki and relevant norms and regulations for clinical research and complied with the EQUATOR network guidelines. This study was approved by the Academic Ethics Committee of Xiang’an Hospital of Xiamen University, School of Medicine, Xiamen University. (Approval number: 2024-114-01). Informed consent to participate was obtained from all of the participants in the study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Hematocrit-Related Alterations of Circulating microRNA-21 Levels in Heart Failure Patients with Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Preliminary Study.Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2021 Apr;25(4):302-306. doi: 10.1089/gtmb.2020.0277. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2021. PMID: 33877895
-
Circulating exosomal miR-92b-5p is a promising diagnostic biomarker of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction patients hospitalized for acute heart failure.J Thorac Dis. 2018 Nov;10(11):6211-6220. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2018.10.52. J Thorac Dis. 2018. PMID: 30622793 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating microRNAs in heart failure with reduced and preserved left ventricular ejection fraction.Eur J Heart Fail. 2015 Apr;17(4):393-404. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.223. Epub 2015 Jan 23. Eur J Heart Fail. 2015. PMID: 25619197
-
Diagnostic performance of microRNAs in the detection of heart failure with reduced or preserved ejection fraction: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Heart Fail. 2022 Dec;24(12):2212-2225. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.2700. Epub 2022 Oct 27. Eur J Heart Fail. 2022. PMID: 36161443 Free PMC article.
-
Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction (HFrEF) and Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF): The Diagnostic Value of Circulating MicroRNAs.Cells. 2019 Dec 16;8(12):1651. doi: 10.3390/cells8121651. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31888288 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rogers C, Bush N. Heart failure: pathophysiology, diagnosis, Medical Treatment guidelines, and nursing management. Nurs Clin North Am. 2015;50(4):787–99. - PubMed
-
- Murphy SP, Ibrahim NE, Januzzi JL Jr. Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: a review. JAMA. 2020;324(5):488–504. - PubMed
-
- Krittanawong C, Rodriguez M, Lui M, Misra A, Tang WHW, Bozkurt B, Yancy CW. Misconceptions and facts about heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. Am J Med. 2023;136(5):422–31. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

