Modified Huangqi Chifeng decoction alleviates podocyte injury on rat with experimental membranous nephropathy
- PMID: 39972601
- PMCID: PMC11843643
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2459896
Modified Huangqi Chifeng decoction alleviates podocyte injury on rat with experimental membranous nephropathy
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to investigate the therapeutic effects of modified Huangqi Chifeng decoction (MHCD) on proteinuria in membranous nephropathy (MN) and its potential protective effects on podocytes. Furthermore, we explored whether these effects are associated with the inhibition of the nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) pathway.
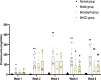
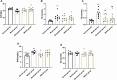
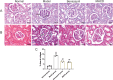
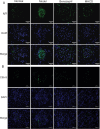
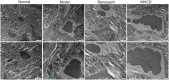
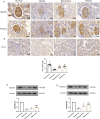
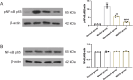
Methods: Passive Heymann nephritis (PHN) rat model was applied with a single tail vein injection of sheep anti-rat Fx1A serum (0.4 ml/100g). All rats were divided into four groups: normal group, PHN group, benazepril group (10 mg/kg), and MHCD group (12.5 g/kg), and were treated for 6 weeks. 24-hour urine protein levels and serum biochemical parameters were measured. Optical microscopy and transmission electron microscopy were performed to assess pathological changes in renal tissues. Additionally, the expression levels of IgG, C5b-9, nephrin, podocin, Wilms' tumor gene 1 (WT-1), and NF-κB p65 were evaluated.
Results: PHN rats exhibited progressive proteinuria over time. However, MHCD treatment significantly reduced levels of proteinuria and triglyceride, while increased levels of albumin. Moreover, MHCD alleviated pathological damage in renal tissues, and reduced the expression of IgG and membrane attack complex (C5b-9). Immunohistochemistry analysis revealed that MHCD increased the expression of nephrin, podocin, and WT-1. Western blot analysis showed that MHCD increased the expression of nephrin and podocin while inhibiting the activation of NF-κB p65.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that MHCD exert reno-protective effects in the experimental rat model of MN by alleviating podocyte damage and inhibiting the NF-κB pathway.
Keywords: Membranous nephropathy; NF-κB pathway; modified Huangqi Chifeng decoction; passive Heymann nephritis; podocyte injury.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protective effect of modified Huangqi Chifeng decoction on immunoglobulin A nephropathy through toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation factor 88/nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway.J Tradit Chin Med. 2024 Apr;44(2):324-333. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240203.001. J Tradit Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 38504538 Free PMC article.
-
Modified Huangqi Chifeng Decoction Attenuates Proteinuria by Reducing Podocyte Injury in a Rat Model of Immunoglobulin a Nephropathy.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jul 26;12:714584. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.714584. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34381367 Free PMC article.
-
Ameliorative effects of Modified Huangqi Chifeng decoction on podocyte injury via autophagy mediated by PI3K/AKT/mTOR and AMPK/mTOR pathways.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Mar 1;321:117520. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117520. Epub 2023 Dec 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38042389
-
Safranal Ameliorates Renal Damage, Inflammation, and Podocyte Injury in Membranous Nephropathy via SIRT/NF-κB Signalling.Curr Med Sci. 2025 Apr;45(2):288-300. doi: 10.1007/s11596-025-00020-8. Epub 2025 Mar 4. Curr Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40035996 Free PMC article.
-
Membranous nephropathy.Contrib Nephrol. 2011;169:107-125. doi: 10.1159/000313948. Epub 2011 Jan 20. Contrib Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21252514 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
