Botulinum Toxin in Aesthetic Medicine: A Bibliometric Analysis of Research Trends and Methodological Quality of the Top 100 Cited Publications
- PMID: 39974503
- PMCID: PMC11836436
- DOI: 10.1093/asjof/ojae131
Botulinum Toxin in Aesthetic Medicine: A Bibliometric Analysis of Research Trends and Methodological Quality of the Top 100 Cited Publications
Abstract
Background: Botulinum toxin is widely used in aesthetic medicine, with numerous studies examining its efficacy and safety.
Objectives: This bibliometric analysis aims to describe research trends and assess the methodological quality of the highest-impact botulinum toxin research in aesthetic applications.
Methods: The authors of this study identified the 100 most-cited publications on botulinum toxin in aesthetics using Web of Science, covering all available journal years (from inception to October 2024). The Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine Level of Evidence (LOE) was used to assess the methodological quality of each study.
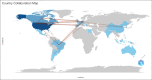
Results: The authors identified 1728 articles on the aesthetic uses of botulinum toxin, with the top 100 most-cited articles spanning from 1994 to 2021. The United States dominated the research landscape with 50 articles, followed by Canada (15). The University of California (United States) and the University of British Columbia (Canada) emerged as the top contributing institutions. Among journals, Dermatologic Surgery led in publication count, followed by Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery and Aesthetics Surgery Journal. Notably, Professors Jean Carruthers and Alastair Carruthers from Canada were the leading researchers, topping both publication count and citation metrics. Notably, more than half of the studies were classified as LOE 5 (Expert Opinion/Narrative Review).
Conclusions: This bibliometric analysis reveals a paucity of high-quality studies in the field of botulinum toxin in aesthetic medicine, with research predominantly concentrated in western countries. These findings highlight the need for more rigorous, evidence-based studies and increased global collaboration to advance the understanding and application of botulinum toxin in aesthetics.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Aesthetic Society.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A bibliometric analysis of sentinel lymph node biopsy in melanoma of the top 90 cited publications.Melanoma Manag. 2025 Dec;12(1):2494979. doi: 10.1080/20450885.2025.2494979. Epub 2025 Apr 28. Melanoma Manag. 2025. PMID: 40289688 Free PMC article.
-
A Bibliometric Analysis of the Top 100 Papers on Gluteal Augmentation.Aesthet Surg J Open Forum. 2024 Jul 8;6:ojae053. doi: 10.1093/asjof/ojae053. eCollection 2024. Aesthet Surg J Open Forum. 2024. PMID: 39100865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global Trends of Botulinum Toxin Literature: A Bibliometric Analysis of Botulinum Toxin Publications Between 1975 and 2017.J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2020 Apr-Jun;13(2):95-102. doi: 10.4103/JCAS.JCAS_111_19. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2020. PMID: 32792770 Free PMC article.
-
Therapies for children with cerebral palsy: A Web of Science-based literature analysis.Neural Regen Res. 2012 Nov 25;7(33):2632-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2012.33.009. Neural Regen Res. 2012. PMID: 25368640 Free PMC article.
-
Publication Trends in Aesthetic Breast Surgery: A Bibliometric Analysis.Aesthet Surg J Open Forum. 2024 Jun 10;6:ojae045. doi: 10.1093/asjof/ojae045. eCollection 2024. Aesthet Surg J Open Forum. 2024. PMID: 39015114 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dorizas A, Krueger N, Sadick NS. Aesthetic uses of the botulinum toxin. Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:23–36. - PubMed
-
- American Society of Plastic Surgeons . Plastic surgery statistics report 2020. Accessed October 30, 2024. Retrieved from https://www.plasticsurgery.org/documents/News/Statistics/2020/plastic-su...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
