Modification approaches of walnut proteins to improve their structural and functional properties: A review
- PMID: 39974719
- PMCID: PMC11838099
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.101873
Modification approaches of walnut proteins to improve their structural and functional properties: A review
Abstract
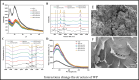
Walnut protein has a high gluten content and compact structure, which limits its water solubility and affects its applications. Therefore, improving the sustainability of walnut proteins is an urgent issue that must be addressed. Physical modification can directly alter the structure of walnut proteins, leading to enhanced functional properties. Chemical modifications typically involve the introduction of exogenous substances that react with walnut proteins to obtain novel products with improved processing attributes. As a highly specific modification technique, biomodification uses enzymes or microorganisms to break down walnut proteins into small peptide molecules or cross-link them to form soluble polymers, thereby enhancing their functional properties and bioactivity. This review presents various methods for modifying walnut proteins and their effects on the structure and functional properties of walnut proteins. The challenges associated with the application and development of these unique technologies are also discussed.
Keywords: Functional properties; Modification technology; Structure; Walnut protein.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Ali U., Kikumoto M., Cui Y., Ciantia M., Previtali M. Role of particle rotation in sheared granular media. Acta Geotechnica. 2023;18(9):4599–4614. doi: 10.1007/s11440-023-01860-1. - DOI
-
- Ashaolu T.J., Lee C.C., Ashaolu J.O., Tarhan O., Pourjafar H., Jafari S.M. Pepsin: An excellent proteolytic enzyme for the production of bioactive peptides. Food Reviews International. 2023;0(0):1–38. doi: 10.1080/87559129.2023.2238814. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

