This is a preprint.
IRF7 controls spontaneous autoimmune germinal center and plasma cell checkpoints
- PMID: 39974943
- PMCID: PMC11838595
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.02.04.636277
IRF7 controls spontaneous autoimmune germinal center and plasma cell checkpoints
Update in
-
IRF7 controls spontaneous autoimmune germinal center and plasma cell checkpoints.J Exp Med. 2025 Jul 7;222(7):e20231882. doi: 10.1084/jem.20231882. Epub 2025 May 27. J Exp Med. 2025. PMID: 40439584
Abstract
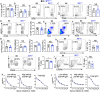
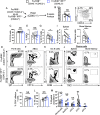
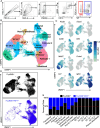
How IRF7 promotes autoimmune B cell responses and systemic autoimmunity is unclear. Analysis of spontaneous SLE-prone mice deficient in IRF7 uncovered the IRF7 role in regulating autoimmune germinal center (GC), plasma cell (PC) and autoantibody responses and disease. IRF7, however, was dispensable for foreign antigen driven GC, PC and antibody responses. Competitive bone marrow (BM) chimeras highlighted the importance of IRF7 in hematopoietic cells in spontaneous GC and PC differentiation. Single-cell-RNAseq of SLE-prone B cells indicated IRF7 mediated B cell differentiation through GC and PC fates. Mechanistic studies revealed that IRF7 promoted B cell differentiation through GC and PC fates by regulating the transcriptome, translation, and metabolism of SLE-prone B cells. Mixed BM chimeras demonstrated a requirement for B cell-intrinsic IRF7 in IgG autoantibody production but not sufficient for promoting spontaneous GC and PC responses. Altogether, we delineate previously unknown B cell-intrinsic and -extrinsic mechanisms of IRF7-promoted spontaneous GC and PC responses, loss of tolerance, autoantibody production and SLE development.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors have no financial conflicts of interests to disclose.
Figures





References
-
- Ban T., Kikuchi M., Sato G.R., Manabe A., Tagata N., Harita K., Nishiyama A., Nishimura K., Yoshimi R., Kirino Y., Yanai H., Matsumoto Y., Suzuki S., Hihara H., Ito M., Tsukahara K., Yoshimatsu K., Yamamoto T., Taniguchi T., Nakajima H., Ito S., and Tamura T.. 2021. Genetic and chemical inhibition of IRF5 suppresses pre-existing mouse lupus-like disease. Nat Commun 12:4379. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Banga J., Srinivasan D., Sun C.C., Thompson C.D., Milletti F., Huang K.S., Hamilton S., Song S., Hoffman A.F., Qin Y.G., Matta B., LaPan M., Guo Q., Lu G., Li D., Qian H., Bolin D.R., Liang L., Wartchow C., Qiu J., Downing M., Narula S., Fotouhi N., DeMartino J.A., Tan S.L., Chen G., and Barnes B.J.. 2020. Inhibition of IRF5 cellular activity with cell-penetrating peptides that target homodimerization. Sci Adv 6:eaay1057. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
