This is a preprint.
Neuronal Activity-Dependent Gene Dysregulation in C9orf72 i3Neuronal Models of ALS/FTD Pathogenesis
- PMID: 39975241
- PMCID: PMC11838197
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.01.27.632228
Neuronal Activity-Dependent Gene Dysregulation in C9orf72 i3Neuronal Models of ALS/FTD Pathogenesis
Update in
-
Neuronal activity-dependent gene dysregulation in C9orf72 i3Neuronal models of ALS/FTD pathogenesis.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2025 Oct 1;329(4):C1085-C1100. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00238.2025. Epub 2025 Aug 28. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40875372
Abstract
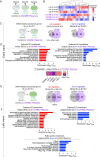
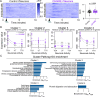
The GGGGCC nucleotide repeat expansion (NRE) mutation in the C9orf72 (C9) gene is the most common cause of ALS and FTD. Neuronal activity plays an essential role in shaping biological processes within both healthy and neurodegenerative disease scenarios. Here, we show that at baseline conditions, C9-NRE iPSC-cortical neurons display aberrations in several pathways, including synaptic signaling and transcriptional machinery, potentially priming diseased neurons for an altered response to neuronal stimulation. Indeed, exposure to two pathophysiologically relevant stimulation modes, prolonged membrane depolarization, or a blockade of K+ channels, followed by RNA sequencing, induces a temporally divergent activity-dependent transcriptome of C9-NRE cortical neurons compared to healthy controls. This study provides new insights into how neuronal activity influences the ALS/FTD-associated transcriptome, offering a dataset that enables further exploration of pathways necessary for conferring neuronal resilience or degeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ababneh NA, Scaber J, Flynn R, Douglas A, Barbagallo P, Candalija A, Turner MR, Sims D, Dafinca R, Cowley SA, Talbot K (2020) Correction of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis related phenotypes in induced pluripotent stem cell-derived motor neurons carrying a hexanucleotide expansion mutation in C9orf72 by CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing using homology-directed repair. Hum Mol Genet 29:2200–2217. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
