This is a preprint.
How the Stroop Effect Arises from Optimal Response Times in Laterally Connected Self-Organizing Maps
- PMID: 39975444
- PMCID: PMC11838785
How the Stroop Effect Arises from Optimal Response Times in Laterally Connected Self-Organizing Maps
Abstract
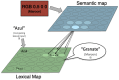
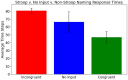
The Stroop effect refers to cognitive interference in a color-naming task: When the color and the word do not match, the response is slower and more likely to be incorrect. The Stroop task is used to assess cognitive flexibility, selective attention, and executive function. This paper implements the Stroop task with self-organizing maps (SOMs): Target color and the competing word are inputs for the semantic and lexical maps, associative connections bring color information to the lexical map, and lateral connections combine their effects over time. The model achieved an overall accuracy of 84.2%, with significantly fewer errors and faster responses in congruent compared to no-input and incongruent conditions. The model's effect is a side effect of optimizing speed-accuracy tradeoffs, and can thus be seen as a cost associated with overall efficient performance. The model can further serve studying neurologically-inspired cognitive control and related phenomena.
Keywords: Cognitive control; Computational modeling; Neural networks; Self-organizing maps; Stroop task.
Figures





References
-
- Abutalebi J., & Green D. (2007). Bilingual language production: The neurocognition of language representation and control. Journal of Neurolinguistics, 20(3), 242–275. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroling.2006.10.003 - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
