A review on conducting organic polymers: Concepts, applications, and potential environmental benefits
- PMID: 39975833
- PMCID: PMC11835703
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e42375
A review on conducting organic polymers: Concepts, applications, and potential environmental benefits
Abstract
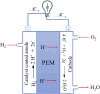
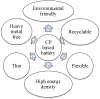
Polymer materials have long been valued for their insulating properties. But recent advancements have revealed their potential as electrically conductive materials, offering an alternative to traditional metallic conductors with the added benefit of reduced environmental impact. This review article provides a comprehensive overview of conducting organic polymers, focusing on their conceptual foundations, diverse applications, and their significant role in mitigating environmental pollution. The paper begins with an exploration of how polymeric materials have progressed from insulators to conductors, explaining the basic principles and mechanisms behind their electrical conductivity. It then provides an insight into the various applications enabled by their unique optical and electronic properties, including their use in light-emitting diodes, electrochromic displays, smart windows, fuel cells, solar cells, supercapacitors and batteries. Additionally, the review emphasizes the potential of conducting organic polymers in mitigating environmental pollution, particularly through their role in wastewater treatment and e-waste management. By examining recent advancements and promising future prospects, this article underscores the potential of conducting organic polymers to revolutionize both electronic technology and environmental sustainability.
Keywords: Adsorption; Conducting polymer; Conduction mechanism; Doping; Fuel cell; Heavy metal; Led; Photocatalysis; Solar cell; Supercapacitor; Wastewater.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures























References
-
- Bahrani S., Hashemi S.A., Mousavi S.M., Arjmand M., Ghalamfarsa F., Ghaedi M. ACS Symposium Series, American Chemical Society. 2022. Conductive polymers in green analytical chemistry; pp. 1–37. - DOI
-
- Das T.K., Prusty S. Review on conducting polymers and their applications. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2012;51:1487–1500. doi: 10.1080/03602559.2012.710697. - DOI
-
- Matula R.A. Electrical resistivity of copper, goid r palladium, and silver’. 1980. http://jpcrd.aip.org/about/rights_and_permissions
-
- Letheby H. On the production of a blue substance by the electrolysis of sulphate of aniline. J. Chem. Soc. 1862;15:161–163. doi: 10.1039/JS8621500161. - DOI
-
- Shirakawa H., Louis E.J., MacDiarmid A.G., Chiang C.K., Heeger A.J. Synthesis of electrically conducting organic polymers: halogen derivatives of polyacetylene, (CH)x. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1977:578–580. doi: 10.1039/C39770000578. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

