Examine the impact of green-synthesized nanomaterials on the germination rates and seedling characteristics of African Marigold (Tagetes erecta L. var. Pusa Narangi Ganda and Pusa Basanti Ganda)
- PMID: 39975837
- PMCID: PMC11835571
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e42319
Examine the impact of green-synthesized nanomaterials on the germination rates and seedling characteristics of African Marigold (Tagetes erecta L. var. Pusa Narangi Ganda and Pusa Basanti Ganda)
Abstract
Background: West Bengal is key to India's flower industry, contributing 10.61 % of total production, with marigolds valued at 63.44 thousand tonnes. To achieve good yields, many farmers heavily use chemical fertilizers and insecticides. Marigold seeds typically germinate in about 14 days, but farmers often face issues with uneven germination and poor seedling quality.
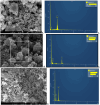
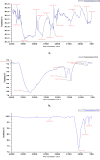
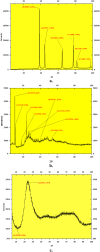
Materials and methods: This study was conducted at ICAR-AICRP on Floriculture and Landscape Architecture, HRS, Mandouri, Bidhan Chandra Krishi Vishwavidyalaya, West Bengal, India. We synthesized nanoparticles from Tulsi, Doob grass, and Hibiscus extracts in the lab and analyzed them using XRD, SEM, FTIR, and DLS-Zeta methods. We prepared different concentrations of TiO2 NP, SiO2 NP, and AgNPs to test their effects on two marigold varieties: Pusa Basanti Ganda and Pusa Narangi Ganda.
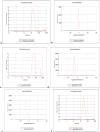
Findings: Recent trial results showed that treatments T4 and T5 achieved the highest germination percentages, between 90.33 % and 96.67 %, due to increased titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NP). The Vigor Index (VI) was lowest in T10 with silver nanoparticles at 521.67, compared to 609.33 for the control group (T0) in Pusa Basanti Ganda. Seeds treated with silver NPs had longer germination times of 4.5-6.4 days, while silica nanoparticles (SiO2 NP) had mean germination times ranging from 4.6 to 5.2 days. The root/shoot ratio positively correlated with shoot dry weight (0.501 at p = 0.05). In Pusa Basanti Ganda, final germination percentage correlated positively with the Germination Rate Index (GRI), Mean Germination Rate (MGR), and Coefficient of Variation (COV) at values of 0.866, 0.756, and 0.743 respectively, all significant at p = 0.01.
Conclusion: The experiment showed that titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles at high concentrations enhance seed germination, while silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) hinder it. Silicon dioxide (SiO2) NPs at moderate concentrations support seedling growth. Tested salts at specific concentrations can be recommended to farmers for better crop production.
Keywords: Germination; Green synthesis; Marigold; Nanoparticles; Seedling vigour.
© 2025 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures







References
-
- Kaushik N., Thakkar M.S., Snehit S., Mhatre M.S., Rasesh Y., Parikh M.S. Biological synthesis of metallic nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2010;6:257–262. - PubMed
-
- Wang X.W., Zhang L., Ma C.L., Song R.Y., Hou H.B., Li D.L. Enrichment and separation of silver from waste solutions by metal ion imprinted membrane. Hydrometal. 2009;100:82–86.
-
- Gokulakrishnan J., Elumalai K., Surya P., Baranitharan M., Rajaganesh K., Irrusappan H., Kudamba A. Tinospora malabarica leaf extract fractions-derived silver nanoparticles and their spectral characterisation: evaluation of their toxicity properties against agricultural pests Spodoptera litura and Helicoverpa armigera. Mater. Technol. 2024;39(1)
-
- Seku K., Hussaini S.S., Reddy G.B., Reddy M.R.K. Nanofungicides. 2024. Silver-based bio fungicides for the suppression of pathogenic fungi in agriculture fields; pp. 169–194.
-
- Zharov V.P., Kim J.W., Curiel D.T., Everts M. Self-assembling nanoclusters in living systems: application for integrated photothermal nanodiagnostics and nanotherapy. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2005;1(4):326–345. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

