This is a preprint.
Integrated Whole Genome and Transcriptome Sequencing as a Framework for Pediatric and Adolescent AML Diagnosis and Risk Assessment
- PMID: 39975890
- PMCID: PMC11838756
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-5775959/v1
Integrated Whole Genome and Transcriptome Sequencing as a Framework for Pediatric and Adolescent AML Diagnosis and Risk Assessment
Update in
-
Clinical experience of using integrated whole genome and transcriptome sequencing as a framework for pediatric and adolescent acute myeloid leukemia diagnosis and risk assessment.Leukemia. 2025 Oct 7. doi: 10.1038/s41375-025-02774-5. Online ahead of print. Leukemia. 2025. PMID: 41057686
Abstract
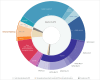
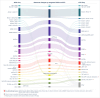
Pediatric acute myeloid leukemia (AML) exhibits distinct genetic characteristics, including unique driver alterations and mutations with prognostic and therapeutic significance. Emerging rare, recurrent genetic abnormalities and their associations with outcomes emphasize the need for high-throughput molecular diagnostic tools. Whole genome sequencing (WGS) reliably detects key AML biomarkers such as structural variants, mutations, and copy number alterations. Whole transcriptome sequencing (WTS) complements WGS by uncovering oncogene expression patterns, allele-specific expression, and gene expression signatures. In this study, we describe an integrated WGS and WTS clinical workflow for routine pediatric AML diagnosis and present a systematic evaluation of its application compared to conventional cytogenetics and standard molecular diagnostic methods. Our findings demonstrate that the integrated WGS and WTS (iWGS-WTS) approach improves the identification of clinically relevant genetic alterations, enhancing precise disease classification and risk assessment. Moreover, with advancements in workflow and bioinformatics pipelines, the testing turnaround time can be optimized to meet the demands of clinical decision-making, positioning iWGS-WTS as a practical and superior alternative to traditional diagnostic methods in pediatric AML management.
Keywords: AML; Whole genome sequencing; Whole transcriptome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
Additional Declarations: There is NO Competing Interest.
Figures




References
-
- Loghavi S, Reville PK, Lachowiez CA, Routbort M, Patel K, Kanagal-Shamanna R et al. (2022) The Adverse Effect of Myelodysplasia-Related Mutations in De Novo Acute Myeloid Leukemia Is Associated with Higher Variant Allelic Frequency (VAF): A Proposal for a Numeric Cutoff for Variant Allelic Frequency. Blood 140(Supplement 1):6306–6308
-
- 5WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board Haematolymphoid tumours. Lyon (France): International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2024. (WHO classification of tumours series, 5th ed.; vol. 11). https://publications.iarc.who.int/637
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

