This is a preprint.
IL-1 signaling enrichment in inflammatory skin disease loci with higher-risk allele frequencies in African ancestry
- PMID: 39975900
- PMCID: PMC11838759
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-5724270/v1
IL-1 signaling enrichment in inflammatory skin disease loci with higher-risk allele frequencies in African ancestry
Abstract
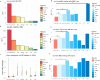
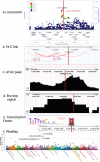
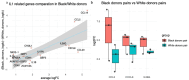
Inflammatory skin diseases (ISDs) exhibit varying prevalence across different ancestry background and geographical regions. Genetic research for complex ISDs has predominantly centered on European Ancestry (EurA) populations and genetic effects on immune cell responses but generally failed to consider contributions from other cell types in skin. Here, we utilized 273 genetic signals from seven different ISDs: acne, alopecia areata (AA), atopic dermatitis (AD), psoriasis, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), systemic sclerosis (SSc), and vitiligo, to demonstrate enriched IL1 signaling in keratinocytes, particularly in signals with higher risk allele frequencies in the African ancestry. Using a combination of ATAC-seq, Bru-seq, and promoter capture Hi-C, we revealed potential regulatory mechanisms of the acne locus on chromosome 2q13. We further demonstrated differential responses in keratinocytes upon IL1β stimulation, including the pro-inflammatory mediators CCL5, IL36G, and CXCL8. Taken together, our findings highlight IL1 signaling in epidermal keratinocytes as a contributor to ancestry-related differences in ISDs.
Keywords: Ancestry Difference; Genetic; Inflammatory Skin Disease; Multi-Omics.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: J.E.G. has served as a consultant to AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Almirall, Celgene, BMS, Janssen, Prometheus, TimberPharma, Galderma, Novatis, MiRagen, AnaptysBio and has received research support from AbbVie, SunPharma, Eli Lilly, Kyowa Kirin, Almirall, Celgene, BMS, Janssen, Prometheus, and TimberPharma. L.C.T. has received support from Galderma and Janssen. R.C.B. took part in an advisory board from Pfizer. JMK has received grant support from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Ventus Therapeutics, Rome Therapeutics, and Janssen. JMK has consulted and/or served on advisory boards for AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, EMD serrano, Exo Therapeutics, Vividion, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Related Biosciences, Biogen, Aurinia Pharmaceuticals, Rome Therapeutics, and Ventus Therapeutics.
Figures


Similar articles
-
JAK3 as an Emerging Target for Topical Treatment of Inflammatory Skin Diseases.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 6;11(10):e0164080. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164080. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27711196 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory bowel disease is associated with an increased risk of inflammatory skin diseases: A population-based cross-sectional study.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Jan;76(1):40-48. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2016.08.022. Epub 2016 Oct 25. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 27793451
-
Cross-Sectional Study of Psoriasis, Atopic Dermatitis, Rosacea, and Alopecia Areata Suggests Association With Cardiovascular Diseases.J Drugs Dermatol. 2023 Jun 1;22(6):576-581. doi: 10.36849/JDD.7424. J Drugs Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37276159
-
Understanding the Intricate Pathophysiology of Psoriasis and Related Skin Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 17;26(2):749. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020749. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of autophagy and their implications in dermatological disorders.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 4;15:1486627. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1486627. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39559368 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

