Lactylation-Driven HECTD2 Limits the Response of Hepatocellular Carcinoma to Lenvatinib
- PMID: 39976163
- PMCID: PMC12005811
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202412559
Lactylation-Driven HECTD2 Limits the Response of Hepatocellular Carcinoma to Lenvatinib
Abstract
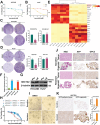
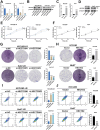
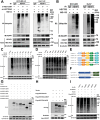
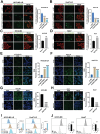
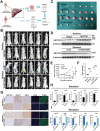
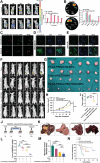
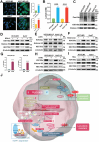
Drug resistance remains a major hurdle for the therapeutic efficacy of lenvatinib in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the underlying mechanisms remain largely undetermined. Unbiased proteomic screening is performed to identify the potential regulators of lenvatinib resistance in HCC. Patient-derived organoids, patient-derived xenograft mouse models, and DEN/CCl4 induced HCC models are constructed to evaluate the effects of HECTD2 both in vitro and in vivo. HECTD2 is found to be highly expressed in lenvatinib-resistant HCC cell lines, patient tissues, and patient-derived organoids and xenografts. In vitro and in vivo experiments demonstrated that overexpression of HECTD2 limits the response of HCC to lenvatinib treatment. Mechanistically, HECTD2 functions as an E3 ubiquitin ligase of KEAP1, which contributes to the degradation of KEAP1 protein. Subsequently, the KEAP1/NRF2 signaling pathway initiates the antioxidative response of HCC cells. Lactylation of histone 3 on lysine residue 18 facilitates the transcription of HECTD2. Notably, a PLGA-PEG nanoparticle-based drug delivery system is synthesized, effectively targeting HECTD2 in vivo. The NPs achieved tumor-targeting, controlled-release, and biocompatibility, making them a promising therapeutic strategy for mitigating lenvatinib resistance. This study identifies HECTD2 as a nanotherapeutic target for overcoming lenvatinib resistance, providing a theoretical basis and translational application for HCC treatment.
Keywords: HECTD2; histone lactylation; nanoparticles; oxidative stress; ubiquitination.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
circCCNY enhances lenvatinib sensitivity and suppresses immune evasion in hepatocellular carcinoma by serving as a scaffold for SMURF1 mediated HSP60 degradation.Cancer Lett. 2025 Mar 1;612:217470. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2025.217470. Epub 2025 Jan 16. Cancer Lett. 2025. PMID: 39826668
-
Ponicidin promotes ferroptosis to enhance treatment sensitivity in Lenvatinib-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma cells through regulation of KEAP1/NRF2.Phytomedicine. 2025 Jul 25;143:156824. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156824. Epub 2025 May 10. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40382941
-
FBXO32 ubiquitination of SUFU promotes progression and lenvatinib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma via hedgehog signaling.Med Oncol. 2025 Mar 11;42(4):98. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02644-1. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40067532
-
New insights into the mechanism of resistance to lenvatinib and strategies for lenvatinib sensitization in hepatocellular carcinoma.Drug Discov Today. 2024 Aug;29(8):104069. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2024.104069. Epub 2024 Jun 25. Drug Discov Today. 2024. PMID: 38936692 Review.
-
Resistance of Lenvatinib in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2022;22(11):865-878. doi: 10.2174/1568009622666220428111327. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2022. PMID: 36267045 Review.
References
-
- Bray F., Laversanne M., Sung H., Ferlay J., Siegel R. L., Soerjomataram I., Jemal A., CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229. - PubMed
-
- Singal A. G., Kanwal F., Llovet J. M., Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 864. - PubMed
-
- Kudo M., Finn R. S., Qin S., Han K.‐H., Ikeda K., Piscaglia F., Baron A., Park J.‐W., Han G., Jassem J., Blanc J. F., Vogel A., Komov D., Evans T. R. J., Lopez C., Dutcus C., Guo M., Saito K., Kraljevic S., Tamai T., Ren M., Cheng A.‐L., Lancet 2018, 391, 1163. - PubMed
-
- Ladd A. D., Duarte S., Sahin I., Zarrinpar A., Hepatology 2023, 1, 926. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82172651/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82472768/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- YD9110002088/USTC Research Funds of the Double First-Class Initiative
- 2022AH020074/Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Education Department for Distinguished Young Scholars
- 2022AH030123/Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Education Department for Excellent Young Scholars
- 2023AH040254/Natural Science Research Project of Anhui Education Department
- 24KJB320006/Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China
- 2022jyxm1733/Provincial Quality Engineering Project of Anhui Education Department
- 2022jyxm1722/Provincial Quality Engineering Project of Anhui Education Department
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
