The endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol is released and transported on demand via extracellular microvesicles
- PMID: 39977325
- PMCID: PMC11873938
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2421717122
The endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol is released and transported on demand via extracellular microvesicles
Abstract
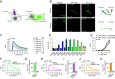
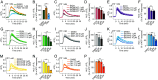
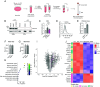
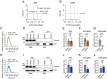
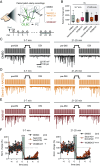
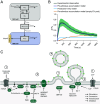
While it is known that endocannabinoids (eCB) modulate multiple neuronal functions, the molecular mechanism governing their release and transport remains elusive. Here, we propose an "on-demand release" model, wherein the formation of microvesicles, a specific group of extracellular vesicles (EVs) containing the eCB, 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), is an important step. A coculture model system that combines a reporter cell line expressing the fluorescent eCB sensor, G protein-coupled receptor-based (GRAB)eCB2.0, and neuronal cells revealed that neurons release EVs containing 2-AG, but not anandamide, in a stimulus-dependent process regulated by protein kinase C, Diacylglycerol lipase, Adenosinediphosphate (ADP) ribosylation factor 6 (Arf6), and which was sensitive to inhibitors of eCB facilitated diffusion. A vesicle contained approximately 2,000 2-AG molecules. Accordingly, hippocampal eCB-mediated synaptic plasticity was modulated by Arf6 and transport inhibitors. The "on-demand release" model, supported by mathematical analysis, offers a cohesive framework for understanding eCB trafficking at the molecular level and suggests that microvesicles carrying signaling lipids in their membrane regulate neuronal functions in parallel to canonical synaptic vesicles.
Keywords: 2-AG; cannabinoid 1 receptors; diacylglycerol lipase; endocannabinoid; extracellular vesicle.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- Piomelli D., Astarita G., Rapaka R., A neuroscientist’s guide to lipidomics. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 8, 743–754 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Marsicano G., et al. , CB1 cannabinoid receptors and on-demand defense against excitotoxicity. Science 302, 84–88 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Kreitzer A. C., Regehr W. G., Retrograde inhibition of presynaptic calcium influx by endogenous cannabinoids at excitatory synapses onto Purkinje cells. Neuron 29, 717–727 (2001). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

