The role of bacterial metabolism in antimicrobial resistance
- PMID: 39979446
- PMCID: PMC12173792
- DOI: 10.1038/s41579-025-01155-0
The role of bacterial metabolism in antimicrobial resistance
Abstract
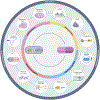
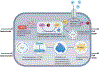
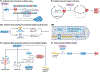
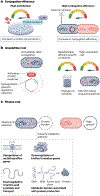
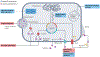
The relationship between bacterial metabolism and antibiotic treatment is complex. On the one hand, antibiotics leverage cell metabolism to function. On the other hand, increasing research has highlighted that the metabolic state of the cell also impacts all aspects of antibiotic biology, from drug efficacy to the evolution of antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Given that AMR is a growing threat to the current global antibiotic arsenal and ability to treat infectious diseases, understanding these relationships is key to improving both public and human health. However, quantifying the contribution of metabolism to antibiotic activity and subsequent bacterial evolution has often proven challenging. In this Review, we discuss the complex and often bidirectional relationships between metabolism and the various facets of antibiotic treatment and response. We first summarize how antibiotics leverage metabolism for their function. We then focus on the converse of this relationship by specifically delineating the unique contribution of metabolism to three distinct but related arms of antibiotic biology: antibiotic efficacy, AMR evolution and AMR mechanisms. Finally, we note the relevance of metabolism in clinical contexts and explore the future of metabolic-based strategies for personalized antimicrobial therapies. A deeper understanding of these connections is crucial for the broader scientific community to address the growing crisis of AMR and develop future effective therapeutics.
© 2025. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Hutchings MI, Truman AW & Wilkinson B Antibiotics: past, present and future. Curr. Opin. Microbiology 51, 72–80 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Blair JMA, Webber MA, Baylay AJ, Ogbolu DO & Piddock LJV Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol 13, 42–51 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Bhargava P & Collins JJ Boosting bacterial metabolism to combat antibiotic resistance. Cell Metab. 21, 154–155 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

