New insights into pulmonary arterial hypertension: interaction between PANoptosis and perivascular inflammatory responses
- PMID: 39979525
- PMCID: PMC12167302
- DOI: 10.1007/s10495-025-02086-0
New insights into pulmonary arterial hypertension: interaction between PANoptosis and perivascular inflammatory responses
Abstract
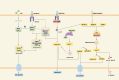
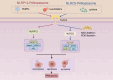
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a heterogeneous disease characterized by various etiologies, with pulmonary vascular remodeling recognized as a main pathological change. Currently, it is widely accepted that vascular remodeling is closely associated with abnormal pulmonary vascular cell death and perivascular inflammation. The simultaneous activation of various pulmonary vascular cell death leads to immune cell adhesion and inflammatory mediator releases; And in turn, the inflammatory response may also trigger cell death and jointly promote the progression of vascular remodeling. Recently, PANoptosis has been identified as a phenomenon that describes the simultaneous activation and interaction of multiple forms of programmed cell death (PCD). Therefore, the relationship between PANoptosis and inflammation in PAH warrants further investigation. This review examines the mechanisms underlying apoptosis, necroptosis, pyroptosis, and inflammatory responses in PAH, with a focus on PANoptosis and its interactions with inflammation. And it aims to elucidate the significance of this emerging form of cell death and inflammation in the pathophysiology of PAH and to explore its potential as a therapeutic target.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Inflammation; Necroptosis; PANoptosis; Pulmonary artery hypertension; Pyroptosis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Caspase-Linked Programmed Cell Death in Prostate Cancer: From Apoptosis, Necroptosis, and Pyroptosis to PANoptosis.Biomolecules. 2023 Nov 28;13(12):1715. doi: 10.3390/biom13121715. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 38136586 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging connectivity of programmed cell death pathways and pulmonary vascular remodelling during pulmonary hypertension.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Aug;28(16):e70003. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70003. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39153207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Panorama of artery endothelial cell dysfunction in pulmonary arterial hypertension.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2024 Dec;197:61-77. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2024.10.004. Epub 2024 Oct 20. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 39437884 Review.
-
A new perspective on targeting pulmonary arterial hypertension: Programmed cell death pathways (Autophagy, Pyroptosis, Ferroptosis).Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Dec;181:117706. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117706. Epub 2024 Nov 23. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 39581144 Review.
-
ZBP1 promotes fungi-induced inflammasome activation and pyroptosis, apoptosis, and necroptosis (PANoptosis).J Biol Chem. 2020 Dec 25;295(52):18276-18283. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015924. Epub 2020 Oct 27. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 33109609 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Editorial: Community series in inflammation in respiratory and neurological diseases and the immune-interaction of the lung-brain axis, volume II.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 12;16:1634921. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1634921. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40574853 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Dynamic and interpretable deep learning model for predicting respiratory failure following cardiac surgery.BMC Anesthesiol. 2025 Aug 5;25(1):394. doi: 10.1186/s12871-025-03239-z. BMC Anesthesiol. 2025. PMID: 40764535 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilkins MR (2022) Pulmonary hypertension: dissecting a complex phenotype. J Am Coll Cardiol 80:719–721. 10.1016/j.jacc.2022.05.039 - PubMed
-
- Maarman GJ, Shaw J, Allwood B (2020) Pulmonary hypertension in majority countries: opportunities amidst challenges. Curr Opin Pulm Med 26:373–383. 10.1097/MCP.0000000000000702 - PubMed
-
- Humbert M, Kovacs G, Hoeper MM, Badagliacca R, Berger RMF, Brida M, Carlsen J, Coats AJS, Escribano-Subias P, Ferrari P, Ferreira DS, Ghofrani HA, Giannakoulas G, Kiely DG, Mayer E, Meszaros G, Nagavci B, Olsson KM, Pepke-Zaba J, Quint JK, Rådegran G, Simonneau G, Sitbon O, Tonia T, Toshner M, Vachiery JL, Vonk Noordegraaf A, Delcroix M, Rosenkranz S, ESC/ERS Scientific Document Group (2022) 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur Heart J 43:3618–3731. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac237 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

