Efficacy of sivelestat in alleviating postoperative pulmonary injury in patients with acute aortic dissection undergoing total arch replacement: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 39979797
- PMCID: PMC11843757
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-025-04527-9
Efficacy of sivelestat in alleviating postoperative pulmonary injury in patients with acute aortic dissection undergoing total arch replacement: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
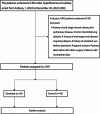
Objective: Sivelestat may reduce postoperative pulmonary injury after total arch replacement (TAR). This study aimed to evaluate whether the preoperative PaO2/FiO2 (P/F) ratio affects the efficacy of sivelestat in reducing postoperative pulmonary injury in patients with acute aortic dissection (AAD) who underwent TAR using deep hypothermic circulatory arrest (DHCA).
Methods: Data of patients with AAD who underwent TAR using DHCA in a tertiary hospital between February 1, 2022, and December 30, 2022, were retrospectively reviewed. The patients were divided into the sivelestat and control groups. Three subgroup analyses were performed based on the postoperative P/F ratio. The primary clinical outcomes were assessed to determine the efficacy and safety of sivelestat in managing postoperative pulmonary dysfunction in patients undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass.
Results: A total of 187 patients were included, with 95 in the sivelestat group and 92 in the control group. No significant differences were found in the clinical variables between the two groups (all P > 0.05), except for some improvements in the inflammatory biomarker levels (including white blood cell count, neutrophil count, and C-reactive protein). Subgroup analysis revealed that sivelestat treatment significantly increased the P/F ratio on the 4th day and 3rd day after TAR in patients with mild lung injury (P = 0.02) and moderate lung injury (P = 0.03), respectively. Additionally, sivelestat reduced the levels of several postoperative inflammatory biomarkers in both subgroups.
Conclusions: Among patients with AAD with mild or moderate preoperative lung injury, defined by a low P/F ratio, sivelestat significantly improved the postoperative P/F ratio and attenuated inflammatory responses after TAR. These findings suggest an important avenue for further research.
Keywords: Hypothermic circulatory arrest; PaO2/FiO2 ratio; Pulmonary injury; Sivelestat; Total arch replacement.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This was a single-center retrospective cohort study. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethical Committee of Xijing Hospital (KY20242093-C-1). The requirement for written consent was waived owing to its retrospective nature. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Clinical trial number: Not applicable.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sivelestat attenuates postoperative pulmonary dysfunction after total arch replacement under deep hypothermia.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2008 Oct;34(4):798-804. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcts.2008.07.010. Epub 2008 Aug 22. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2008. PMID: 18722781
-
Protective effect of sivelestat sodium (Eraspol) on postoperative lung dysfunction in patients with type A acute aortic dissection: a pilot study.J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2008 Oct;49(5):627-31. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2008. PMID: 18670380
-
Moderate and deep hypothermic circulatory arrest has a comparable effect on acute kidney injury after total arch replacement with frozen elephant trunk procedure in type A aortic dissection.Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2019 Jul 1;29(1):130-136. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivz092. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2019. PMID: 30977797
-
The effect of sivelestat sodium hydrate on severe respiratory failure after thoracic aortic surgery with deep hypothermia.Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011;17(4):369-75. doi: 10.5761/atcs.oa.10.01555. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011. PMID: 21881324 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Deep Hypothermic Circulatory Arrest Versus Moderate Hypothermic Circulatory Arrest in Aortic Arch Surgery on Postoperative Renal Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Oct 20;9(19):e017939. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.017939. Epub 2020 Sep 29. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 32990132 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hagan PG, Nienaber CA, Isselbacher EM, Bruckman D, Karavite DJ, Russman PL, Evangelista A, Fattori R, Suzuki T, Oh JK, et al. The International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection (IRAD): new insights into an old disease. JAMA. 2000;283(7):897–903. - PubMed
-
- Malaisrie SC, Szeto WY, Halas M, Girardi LN, Coselli JS, Sundt TM 3rd, Chen EP, Fischbein MP, Gleason TG, Okita Y, et al. 2021 the American Association for Thoracic Surgery expert consensus document: surgical treatment of acute type a aortic dissection. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2021;162(3):735–e758732. - PubMed
-
- Nteliopoulos G, Nikolakopoulou Z, Chow BHN, Corless R, Nguyen B, Dimarakis I. Lung injury following cardiopulmonary bypass: a clinical update. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2022;20(11):871–80. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials