The ATLAS/NOA-29 study protocol: a phase III randomized controlled trial of anterior temporal lobectomy versus gross-total resection in newly-diagnosed temporal lobe glioblastoma
- PMID: 39979825
- PMCID: PMC11843818
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-025-13682-3
The ATLAS/NOA-29 study protocol: a phase III randomized controlled trial of anterior temporal lobectomy versus gross-total resection in newly-diagnosed temporal lobe glioblastoma
Abstract
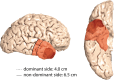
Background: The discovery of cellular tumor networks in glioblastoma, with routes of malignant communication extending far beyond the detectable tumor margins, has highlighted the potential of supramarginal resection strategies. Retrospective data suggest that these approaches may improve long-term disease control. However, their application is limited by the proximity of critical brain regions and vasculature, posing challenges for validation in randomized trials. Anterior temporal lobectomy (ATL) is a standardized surgical procedure commonly performed in patients with pharmacoresistant temporal lobe epilepsy. Translating the ATL approach from epilepsy surgery to the neuro-oncological field may provide a model for investigating supramarginal resection in glioblastomas located in the anterior temporal lobe.
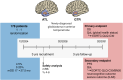
Methods: The ATLAS/NOA-29 trial is a prospective, multicenter, multinational, phase III randomized controlled trial designed to compare ATL with standard gross-total resection (GTR) in patients with newly-diagnosed anterior temporal lobe glioblastoma. The primary endpoint is overall survival (OS), with superiority defined by significant improvements in OS and non-inferiority in the co-primary endpoint, quality of life (QoL; "global health" domain of the European organization for research and treatment of cancer (EORTC) QLQ-C30 questionnaire). Secondary endpoints include progression-free survival (PFS), seizure outcomes, neurocognitive performance, and the longitudinal assessment of six selected domains from the EORTC QLQ-C30 and BN20 questionnaires. Randomization will be performed intraoperatively upon receipt of the fresh frozen section result. A total of 178 patients will be randomized in a 1:1 ratio over a 3-year recruitment period and followed-up for a minimum of 3 years. The trial will be supervised by a Data Safety Monitoring Board, with an interim safety analysis planned after the recruitment of the 57th patient to assess potential differences in modified Rankin Scale (mRS) scores between the treatment arms 6 months after resection. Assuming a median improvement in OS from 17 to 27.5 months, the trial is powered at > 80% to detect OS differences with a two-sided log-rank test at a 5% significance level.
Discussion: The ATLAS/NOA-29 trial aims to determine whether ATL provides superior outcomes at equal patients' Qol compared to GTR in anterior temporal lobe glioblastoma, potentially establishing ATL as the surgical approach of choice for isolated temporal glioblastoma and redefining the standard of care for this patient population.
Trial registration: German Clinical Trials Register (DRKS00035314), registered on October 18, 2024.
Keywords: Anterior temporal lobectomy; Epilepsy surgery; Gross-total resection; Supramarginal resection; Temporal lobe glioblastoma.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The ATLAS/NOA-29 trial protocol has been approved by the local ethics committee of the University Hospital Bonn (reference number: 290/23). The trial complies with the guidelines and regulations outlined in the Berufsordnung für Ärzte, the Declaration of Helsinki, the Datenschutz-Grundverordnung (DSGVO), and the Gesundheitsdatenschutzgesetz (GDSG) of the state of North Rhine-Westphalia, as confirmed by the ethics committee of the University Hospital Bonn. Written informed consent will be obtained from all participants prior to their inclusion in the trial. Consent for publication: All authors agreed to the publication of the manuscript. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Stummer W, Pichlmeier U, Meinel T, Wiestler OD, Zanella F, Reulen HJ, et al. Fluorescence-guided surgery with 5-aminolevulinic acid for resection of malignant glioma: a randomised controlled multicentre phase III trial. Lancet Oncol. 2006;7(5):392–401. - PubMed
-
- Silbergeld DL, Chicoine MR. Isolation and characterization of human malignant glioma cells from histologically normal brain. J Neurosurg. 1997;86(3):525–31. - PubMed
-
- Kageji T, Nagahiro S, Uyama S, Mizobuchi Y, Toi H, Nakamura M, et al. Histopathological findings in autopsied glioblastoma patients treated by mixed neutron beam BNCT. J Neurooncol. 2004;68(1):25–32. - PubMed
-
- Osswald M, Jung E, Sahm F, Solecki G, Venkataramani V, Blaes J, et al. Brain tumour cells interconnect to a functional and resistant network. Nature. 2015;528(7580):93–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

