New horizons for the therapeutic application of nanozymes in cancer treatment
- PMID: 39979897
- PMCID: PMC11844087
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-025-03185-5
New horizons for the therapeutic application of nanozymes in cancer treatment
Abstract
The advent of nanozymes has revolutionized approaches to cancer diagnosis and therapy, introducing innovative strategies that address the limitations of conventional treatments. Nanozyme nanostructures with enzyme-mimicking catalytic abilities exhibit exceptional stability, biocompatibility, and customizable functions, positioning them as promising tools for cancer theranostics. By emulating natural enzyme reactions, nanozymes can selectively target and eradicate cancer cells, minimizing harm to adjacent healthy tissues. Nanozymes can also be functionalized with specific targeting ligands, allowing for the precise delivery and regulated release of therapeutic agents, improving treatment effectiveness and reducing adverse effects. However, issues such as biocompatibility, selectivity, and regulatory compliance remain critical challenges for the clinical application of nanozymes. This review provides an overview of nanozymes, highlighting their unique properties, various classifications, catalytic activities, and diverse applications in cancer treatments. The strategic oncological deployment of nanozymes could profoundly impact future advancements in personalized medicine, highlighting recent progress and prospective directions in enzyme-mimetic approaches for cancer treatment. This review summarizes an overview of nanozymes, highlighting their unique properties, various classifications, catalytic activities, and diverse applications in cancer treatments.
Keywords: Nanomaterials; Reactive-oxygen species; Therapy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: All the authors consent to publication. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



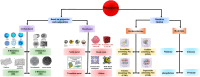


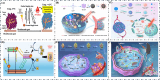



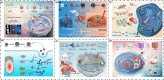
References
-
- Sharmiladevi P, Girigoswami K, Haribabu V, Girigoswami A. Nano-enabled theranostics for cancer. Mater Adv. 2021;2(9):2876–91. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

