Lifestyle intervention to prevent type 2 diabetes after a pregnancy complicated by gestational diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis update
- PMID: 39980013
- PMCID: PMC11844165
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-025-01606-x
Lifestyle intervention to prevent type 2 diabetes after a pregnancy complicated by gestational diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis update
Abstract
Background: Women with prior gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) are at increased risk of type 2 diabetes, and lifestyle intervention (LSI) offered a decade after pregnancy is effective in preventing diabetes. However, since diabetes frequently onsets in the initial years following pregnancy, preventive actions should be implemented closer to pregnancy. We aimed to assess the effect of lifestyle interventions, compared to standard care, in reducing the incidence of diabetes following a pregnancy complicated by GDM.
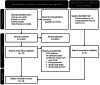
Methods: We searched the Cochrane Library, Embase, MEDLINE, and Web of Science from inception to July 21, 2024, to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) testing LSI to prevent diabetes following gestational diabetes. We followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. We evaluated the risk of bias with the Cochrane Collaboration Risk of Bias tool RoB-2 and the certainty of the evidence with GRADE methodology. We used the DerSimonian-Laird random effects pooling method and evaluated heterogeneity with the I2 statistic and the Chi2 test.
Results: We identified 24 studies involving 9017 women. In studies without high risk of bias (18 studies; 8,357 women), LSI reduced the incidence of diabetes by 19% (RR = 0.81; 95%CI 0.71.0.93). The effect was significant and more protective (RR = 0.78; 0.65, 0.94) in studies evaluating women with GDM identified specifically as at a higher risk of diabetes, compared to those intervening on women with GDM irrespective of risk (RR = 0.85; 0.70, 1.04). Similarly, when expressed in absolute terms, the overall number needed to treat (NNT) was 56 considering all studies, 71 for women with GDM irrespective of risk, and 31 for women with GDM at high risk. The intervention produced a lower weight gain (mean difference=-0.88 kg;-1.52, -0.23 for all studies; -0.62 kg;-1.22, -0.02 for studies without high risk of bias). The effects were robust in sensitivity analyses and supported by evidence of moderate certainty for diabetes and weight change.
Conclusions: LSI offered to women with GDM following pregnancy is effective in preventing type 2 diabetes, despite the small postpartum weight change. The impact of LSI on incidence reduction was greater for women with GDM at a higher diabetes risk.
Prospero: Registration number CRD42024555086, Jun 28, 2024.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; Gestational diabetes; Lifestyle; Meta-analysis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This is a systematic review with meta-analysis. We do not report original data; therefore, requirements related to ethics approval and consent to participate do not apply. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF diabetes atlas. 10th ed. Brussels: IDF; 2021.
-
- The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology. Alarming rise in young-onset type 2 diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2024;12:433. - PubMed
-
- Tuomilehto J, Lindstrom J, Eriksson JG, Valle TT, Hamalainen H, Ilanne-Parikka P, et al. Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1343–50. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

