Deoxynivalenol modulated mucin expression and proinflammatory cytokine production, affecting susceptibility to enteroinvasive Escherichia coli infection in intestinal epithelial cells
- PMID: 39980277
- PMCID: PMC11842951
- DOI: 10.1111/1750-3841.70079
Deoxynivalenol modulated mucin expression and proinflammatory cytokine production, affecting susceptibility to enteroinvasive Escherichia coli infection in intestinal epithelial cells
Abstract
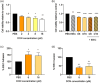
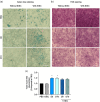
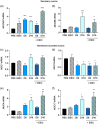
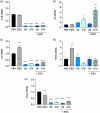
Deoxynivalenol (DON) is a common mycotoxin in crops that could induce intestinal inflammation, affecting the susceptibility of intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) to pathogen infection. This study aimed to investigate DON's effects on mucin and cytokine production as part of the local immune system and how it affected intestinal susceptibility to pathogen infection. Caco-2 cells were exposed to DON followed by acute enteroinvasive Escherichia coli (EIEC) infection. An increase in EIEC attachment to DON-exposed cells was observed, probably in part, mediated by secretory MUC5AC mucins and membrane-bound MUC4 and MUC17 mucins. Additionally, DON with EIEC posttreatment led to significant changes in the gene expression of several proinflammatory cytokines (IL1α, IL1β, IL6, IL8, TNFα, and MCP-1), which may be in part, mediated by NK-κB and/or MAPK signaling pathways. These data suggested DON may exert immunomodulatory effects on IECs, altering the IEC susceptibility to bacterial infection. PRACTICAL APPLICATION: The results suggested that DON might modulate immune responses by affecting mucus and cytokine production, which may affect the susceptibility of intestinal epithelial cells to pathogen infection.
Keywords: bacterial infection; deoxynivalenol; enteroinvasive Escherichia coli; inflammatory responses; mucins.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Food Science published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Institute of Food Technologists.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aggarwal, B. B. , Takada, Y. , Shishodia, S. , Gutierrez, A. M. , Oommen, O. V. , Ichikawa, H. , Baba, Y. , & Kumar, A. (2004). Nuclear transcription factor NF‐kappa B: Role in biology and medicine. Indian Journal of Experimental Biology, 42, 341–353. - PubMed
-
- Alassane‐Kpembi, I. , Puel, O. , Pinton, P. , Cossalter, A.‐M. , Chou, T.‐C. , & Oswald, I. P. (2017). Co‐exposure to low doses of the food contaminants deoxynivalenol and nivalenol has a synergistic inflammatory effect on intestinal explants. Archives of Toxicology, 91, 2677–2687. - PubMed
-
- Antonissen, G. , Van Immerseel, F. , Pasmans, F. , Ducatelle, R. , Janssens, G. P. J. , De Baere, S. , Mountzouris, K. C. , Su, S. , Wong, E. A. , De Meulenaer, B. , Verlinden, M. , Devreese, M. , Haesebrouck, F. , Novak, B. , Dohnal, I. , Martel, A. , & Croubels, S. (2015). Mycotoxins deoxynivalenol and fumonisins alter the extrinsic component of intestinal barrier in broiler chickens. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 63, 10846–10855. - PubMed
-
- Awuchi, C. G. , Ondari, E. N. , Ogbonna, C. U. , Upadhyay, A. K. , Baran, K. , Okpala, C. O. R. , Korzeniowska, M. , & Guiné, R. P. (2021). Mycotoxins affecting animals, foods, humans, and plants: Types, occurrence, toxicities, action mechanisms, prevention, and detoxification strategies—A revisit. Foods, 10, 1279. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

