Brain natriuretic peptide is a biomarker of atrial fibrillation in hemodialysis patients
- PMID: 39980306
- PMCID: PMC11849019
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2463563
Brain natriuretic peptide is a biomarker of atrial fibrillation in hemodialysis patients
Abstract
Objectives: Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common persistent arrhythmia and has adverse outcomes in hemodialysis patients. It is obscure the relationship between BNP and AF in hemodialysis patients. This study investigated the interventionable predictors of AF in hemodialysis patients.
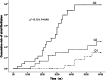
Methods: In this retrospectively observational cohort study, a total of 205 hemodialysis patients were screened and 140 were enrolled. The anthropometrics, laboratory parameters, electrocardiogram and echocardiogram were collected. The patients were divided into three groups based on the tertiles of BNP value. Kaplan-Meier curves were used to compare the incidence of AF among different BNP groups. Restricted cubic spline curves and receiver operator characteristic curves were drawn, and Cox proportional hazards models were applied to identify the predictive value of BNP and the other related factors for incident AF.
Results: During the 5-year follow-up period, 33 (23.6%) individuals developed incident AF. The incidence of AF increased significantly with an increase in the BNP. Cox proportional hazards models indicated that age, dialysis vintage, left atrial diameter, ultrafiltration rate, hs-CRP and BNP were independent risk factors for incident AF. The hazard ratios of BNP (per 100 pg/mL) were 1.038 (95% confidence interval, 1.012-1.064, p = 0.004). BNP had a predictive value for the occurrence of AF (area under the curve = 0.734).
Conclusions: BNP was a good predictor of incident AF in hemodialysis patients. Higher BNP had an increasing adverse event rate of AF. Further research should be needed to clarify the best reference range of BNP in hemodialysis patients.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; brain natriuretic peptide; hemodialysis; predictor; ultrafiltration rate.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s)
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dialysis-specific factors and incident atrial fibrillation in hemodialysis patients.Ren Fail. 2020 Nov;42(1):785-791. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2020.1801467. Ren Fail. 2020. PMID: 32779958 Free PMC article.
-
Brain natriuretic peptide between traditional and nontraditional risk factors in hemodialysis patients: analysis of cardiovascular mortality in a two-year follow-up.Nephron Clin Pract. 2011;119(2):c162-70. doi: 10.1159/000327615. Epub 2011 Jul 8. Nephron Clin Pract. 2011. PMID: 21757955
-
Elevated B-type natriuretic peptide level as a marker of subsequent thromboembolic events in patients with atrial fibrillation.Heart Vessels. 2011 Sep;26(5):530-5. doi: 10.1007/s00380-010-0084-2. Epub 2010 Dec 25. Heart Vessels. 2011. PMID: 21188387
-
Effectiveness of brain natriuretic peptide in predicting postoperative atrial fibrillation in patients undergoing non-cardiac thoracic surgery.Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2015 May;20(5):654-7. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivu454. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2015. PMID: 25630332 Review.
-
Plasma B-type natriuretic peptide levels predict postoperative atrial fibrillation in patients undergoing cardiac surgery.Circulation. 2004 Jul 13;110(2):124-7. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000134481.24511.BC. Epub 2004 Jun 21. Circulation. 2004. PMID: 15210589 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
