Evaluation of polyherbal synergy against diabetes: in-vitro analysis
- PMID: 39980351
- PMCID: PMC11849915
- DOI: 10.1080/20565623.2025.2468128
Evaluation of polyherbal synergy against diabetes: in-vitro analysis
Abstract
Aims: To evaluate the anti-diabetic properties of a polyherbal formulation consisting of Curcuma longa, Emblica officinalis, and Trigonella foenum-graecum through in-vitro assays, and investigate its synergistic effects on glucose metabolism, lipid metabolism, and insulin function.
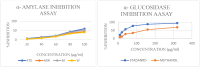
Materials and methods: The polyherbal extract was prepared using methanol, water, and methanol-water as solvents. In-vitro antioxidant (DPPH, Phosphomolybdenum) and anti-diabetic (α-amylase, α-glucosidase inhibition, yeast glucose uptake, and inhibitory glucose diffusion) assays were conducted. L6 rat skeletal muscle cells were used for MTT assay and glucose uptake.
Results: The methanol extract showed the highest antioxidant and anti-diabetic activities compared to aqueous and hydroalcoholic extracts. The IC50 values in DPPH and α-amylase inhibition assays were close to standard drugs, while the MTT assay demonstrated moderate cytotoxicity, confirming the extract's safety. Glucose uptake increased significantly, particularly in L6 cells treated with the methanolic extract.
Conclusion: The polyherbal formulation exhibited potent anti-diabetic properties, particularly the methanolic extract, showing significant glucose regulation and insulin function improvement. This formulation holds promise as a natural treatment for diabetes.
Keywords: Curcuma longa; Emblica officinalis; Polyherbal formulation; Trigonella foenum-graecum; anti-diabetic; glucose uptake.
Plain language summary
This study talks about using natural plants to help with diabetes: An illness where you have too much sugar (or blood sugar) in your blood. Blood: a fluid in your body that carries things that are needed for your body to work well, such as vitamins, minerals, and oxygen to cells. It also takes waste products away. Also called diabetes mellitus. Type 1 diabetes happens most often in kids or young adults. Type 2 usually occurs when you are older. Type 1 diabetes is also called juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes. Insulin is something made by a gland that helps with digestion (your pancreas) and helps blood sugar (glucose) get into your body’s cells. The scientists mixed three plants: turmeric, amla (a fruit), and fenugreek (a seed used in cooking). They made a special plant extract using methanol, which worked better than water. They tested this mix in the lab to see if it could help the body use sugar better and stop certain enzymes that make sugar levels rise too quickly. The results were good! The mix had strong powers to fight harmful molecules (antioxidants) and helped manage sugar. Even though this is exciting, more tests on animals and people are needed to be sure it works safely.
Conflict of interest statement
Financial disclosure
The authors have no relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants, or patents received or pending, or royalties.
Writing disclosure
No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures




References
-
- Williams JM, Poudel B, Shields CA.. Sex differences in autoimmune type-1 diabetes. In sex differences in cardiovascular physiology and pathophysiology. United States: Academic Press; 2019. p. 239–249. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-813197-8.00015-4 - DOI
Annotated reference
-
- Butalia S, et al. ; 2016. * – "Environmental risk factors and type 1 diabetes: past, present and future." - Considerable Interest: This reference explores the environmental factors contributing to diabetes, critical for understanding the disease’s onset and aiding in prevention strategies.
-
- Tilburt JC, Kaptchuk TJ.; 2008. ** – "Herbal medicine research and global health: an ethical analysis." - Of Interest: This study provides ethical insights into herbal medicine research, underscoring the importance of global health perspectives in the development of polyherbal treatments. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gauttam VK, Kalia AN.; 2013. – "Development of polyherbal antidiabetic formulation encapsulated in the phospholipids vesicle system." - Considerable Interest: It highlights the advancements in polyherbal formulations, essential to the context of the current report’s focus on innovative herbal combinations. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mehta S, et al. ; 2009. * – "Anti-diabetic activity of Emblica officinalis in animal models." - Of Interest: This is significant as it directly supports the therapeutic potential of Emblica officinalis, a key component of the polyherbal extract investigated.
-
- Chavda BP, Sharma A.; 2017. ** – "Efficacy of combination of Fenugreek, Amla, and Turmeric powder to reduce blood glucose level among diabetics." - Of Interest: This reference is vital for supporting the synergistic effects of the herbs studied in the polyherbal extract.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
