Qing-Xin-Jie-Yu Granule attenuates myocardial infarction-induced inflammatory response by regulating the MK2/TTP pathway
- PMID: 39980416
- PMCID: PMC11849043
- DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2025.2467377
Qing-Xin-Jie-Yu Granule attenuates myocardial infarction-induced inflammatory response by regulating the MK2/TTP pathway
Abstract
Context: Qing-Xin-Jie-Yu Granule (QXJYG) has shown promise in the treatment of myocardial infarction. However, the mechanism of action of QXJYG underlying its anti-inflammation remain unknown.
Objective: The study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness and mechanism of QXJYG in a mouse model of myocardial infarction and hypoxia-induced H9C2 cells.
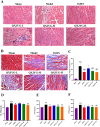
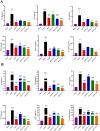
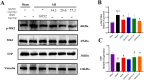
Materials and methods: Myocardial infarction was induced in mice via left anterior descending coronary artery ligation, and hypoxia-induced H9C2 cells was served as the in vitro model. The cardiac function was evaluated by echocardiography, while myocardial tissue pathology was examined using HE and Masson's trichrome staining. Changes in serum markers of cardiac injury were measured using ELISA kits. The levels of inflammatory cytokines in both the serum and cardiac tissue were quantified using the Bio-Plex Pro Mouse Chemokine assay, and hypoxia-induced inflammatory factors in H9C2 cells were assessed by RT-qPCR. Additionally, western blot analysis was conducted to evaluate the expression of proteins related to the MK2/TTP signaling pathway both in vivo and in vitro experiments.
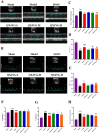
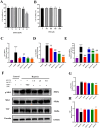
Results: QXJYG significantly enhanced cardiac function in mice with myocardial infarction, as evidenced by improved myocardial tissue structure, reduced collagen fiber deposition, and lowered serum levels of creatine kinase isoenzyme MB (CK-MB), cardiac Troponin T (cTnT), and brain Natriuretic Peptide (BNP). QXJYG may reduce the expression of inflammatory factors in both the heart and serum of myocardial infarction-induced mice and attenuate hypoxia-induced levels of inflammatory factors in cardiomyocytes by decreasing the ratio of p-MK2/MK2 and increasing the protein expression of TTP.
Discussion and conclusions: QXJYG improved cardiac function and reduced injury, fibrosis, and inflammation after myocardial infarction, likely through modulation of the MK2/TTP signaling pathway.
Keywords: Ischemic heart disease; inflammation-induced injury; traditional Chinese medicine formula.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Cao C, Wang R, Gao D, Zhou Y, Lv Y, Ma L.. 2021. Therapeutic efficacy of Gui Feng Tong Yu Tang combined with western drugs in the treatment of acute myocardial infarction and its effect on patients’ blood rheological indexes and cardiac function. Shanxi J Tradit Chin Med. 42(10):1382–1384. Chinese.
-
- Chang X, Li Y, Liu J, Wang Y, Guan X, Wu Q, Zhou Y, Zhang X, Chen Y, Huang Y, et al. 2023. β-tubulin contributes to Tongyang Huoxue decoction-induced protection against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injury of sinoatrial node cells through SIRT1-mediated regulation of mitochondrial quality surveillance. Phytomedicine. 108:154502. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154502. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
