Global, regional, national prevalence, mortality, and disability-adjusted life-years of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and trend analysis from 1990 to 2021 and prediction to 2045
- PMID: 39980558
- PMCID: PMC11839636
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1523169
Global, regional, national prevalence, mortality, and disability-adjusted life-years of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and trend analysis from 1990 to 2021 and prediction to 2045
Abstract
Background: A serious worldwide health concern is cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC). For the purpose of creating focused strategies, it is essential to comprehend geographical variations in cSCC prevalence and trends.
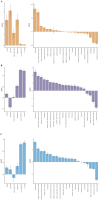
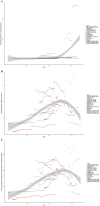
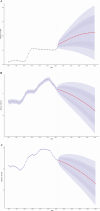
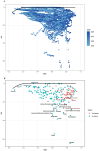
Methods: This study utilized data from the 2021 Global Burden of Diseases (GBD) survey to analyze cSCC across 204 countries and territories. We assessed the age-standardized prevalence rate (ASPR), mortality rate (ASMR), disability-adjusted life years (ASDR), and estimated annual percentage changes (EAPCs), with trends stratified by region, country, age, sex, and Sociodemographic Index (SDI). To evaluate disparities in cSCC burden, we combined the SDI with the inequality slope and concentration indices for an international health inequality analysis. Decomposition analysis assessed the effects of population growth, aging, and epidemiological trends on disease burden, while frontier analysis linked cSCC outcomes with socio-demographic development. A Bayesian Age-Period-Cohort (BAPC) model projected future prevalence, mortality, and DALYs, identifying key drivers of cSCC burden.
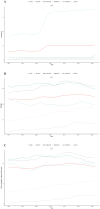
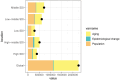
Results: In 2021, there were 2,275,834 cases of cSCC globally, reflecting a 345% increase since 1990. During this period, the ASPR rose from 14.69 to 26.85 per 100,000, while the ASMR increased slightly from 0.67 to 0.69 per 100,000. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) rose from 544,973 to 1,210,874. Among socio-demographic regions, the high SDI region had the highest ASPR, while the middle SDI region exhibited the highest ASMR and ASDR. Decomposition analysis identified population growth and demographic aging as key drivers of the rising ASMR. Countries like Georgia showed significant disparities in frontier analysis, indicating potential for better cSCC management. Health inequality analysis confirmed that the burden was concentrated in nations with higher SDI. By 2045, the global ASPR is projected to reach 64.66, with the ASMR and ASDR expected to decrease to 1.02 and 20.63 per 100,000, respectively.
Conclusion: Over the last three decades, the global burden of cSCC has increased significantly. While mortality rates and DALYs are expected to decline over the next twenty years, the prevalence of cSCC is projected to remain high. This highlights the urgent need to reevaluate preventive efforts aimed at reducing morbidity, particularly in areas with substantial populations over the age of 95.
Keywords: bayesian age-period-cohort (BAPC) model; cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma; decomposition analysis; frontier analysis; global burden of disease; inequality analysis.
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Liu, Cao, Li, Xin and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Global, regional, and national burden of cutaneous malignant melanoma from 1990 to 2021 and prediction to 2045.Front Oncol. 2024 Dec 24;14:1512942. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1512942. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39777336 Free PMC article.
-
The global, regional, and national burden of paralytic ileus and intestinal obstruction, 1990 to 2021: a cross-sectional analysis from the 2021 global burden of disease study.Int J Surg. 2025 Feb 1;111(2):1773-1787. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000002189. Int J Surg. 2025. PMID: 39784557
-
Global, regional, and national burden of gastritis and duodenitis from 1990 to 2021 with projections to 2050: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021.Int J Med Sci. 2025 May 10;22(11):2570-2582. doi: 10.7150/ijms.109762. eCollection 2025. Int J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40520897 Free PMC article.
-
Global, regional, and national burdens of pancreatic cancer attributable to smoking from 1990 to 2021 and the projections to 2035:a systematic analysis from the global burden of disease study 2021.Front Oncol. 2025 May 30;15:1547029. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1547029. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40519307 Free PMC article.
-
Global burden, risk factors, and projections of early-onset dementia: Insights from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021.Ageing Res Rev. 2025 Feb;104:102644. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102644. Epub 2024 Dec 17. Ageing Res Rev. 2025. PMID: 39701185 Review.
Cited by
-
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Vulva in Geriatric With Clinical Features of Papillomatous Plaque Resembling Anogenital Warts Caused by Human Papillomavirus Types 6 and 11.Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2025 Aug 27;2025:1730469. doi: 10.1155/crdm/1730469. eCollection 2025. Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2025. PMID: 40909382 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Complement Factor H: A Marker for Progression and Outcome Prediction Towards Immunotherapy in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jun 26;17(13):2162. doi: 10.3390/cancers17132162. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40647461 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang W, Zeng W, Jiang A, He Z, Shen X, Dong X, et al. . Global, regional and national incidence, mortality and disability-adjusted life-years of skin cancers and trend analysis from 1990 to 2019: An analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Cancer Med. (2021) 10:4905–22. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4046 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Elliott BM, Douglass BR, McConnell D, Johnson B, Harmston C. Incidence, demographics and surgical outcomes of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma diagnosed in Northland, New Zealand. N Z Med J. (2018) 131:61–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

