Staphylococcus aureus-specific TIGIT+ Treg are present in the blood of healthy subjects - a hurdle for vaccination?
- PMID: 39981298
- PMCID: PMC11840346
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1500696
Staphylococcus aureus-specific TIGIT+ Treg are present in the blood of healthy subjects - a hurdle for vaccination?
Abstract
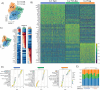
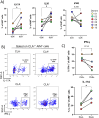
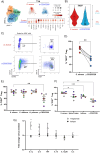
Staphylococcus aureus poses an enormous burden of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Making an efficacious vaccine has however proven extremely challenging. Due to colonizing interactions, pre-existing S. aureus-specific CD4+ T cells are often found in the human population and yet a detailed characterization of their phenotypes and how they might in turn impact vaccine efficacy are thus far unknown. Using an activation induced marker assay to sort for S. aureus-specific CD4+ T cells in an effector function-independent manner, single cell transcriptomic analysis was conducted. Remarkably, S. aureus-specific CD4+ T cells consisted not only of a broader spectrum of conventional T cells (Tcon) than previously described but also of regulatory T cells (Treg). As compared to polyclonally-activated CD4+ T cells, S. aureus-specific Tcon were enriched for the expression of the Th17-type cytokine genes IL17A, IL22 and IL26, while higher percentages of S. aureus-specific Treg expressed the T Cell Immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains (TIGIT), a pleiotropic immune checkpoint. Notably, the antagonistic anti-TIGIT mAb Tiragolumab increased IL-1β production in response to S. aureus in vitro. Therefore, these results uncover the presence of S. aureus-specific TIGIT+ Treg in the blood of healthy subjects that could blunt responses to vaccination and indicate TIGIT as a potential targetable biomarker to overcome pre-exposure-induced immunosuppression.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; TIGIT; Th17; Treg; colonization; host-pathogen interactions; vaccines.
Copyright © 2025 Clegg, Mnich, Carignano, Cova, Tavarini, Sammicheli, Clemente, Smith, Siena, Bardelli, Brazzoli, Bagnoli, McLoughlin and Soldaini.
Conflict of interest statement
GC, ST, CS, BC, ESi, MBa, MBr, FB, and ESo are employees of the GSK group of companies. JC, MM and MS were PhD student at GSK at the time of the study. AC and GC were part of the Scientific Leadership Program at GSK Vaccines at the time of the study. FB is listed as inventor on patents of S. aureus vaccine candidates owned by GSK. BC, ESi, MBa, MBr, FB, and ESo and report ownership of GSK shares and/or restricted GSK shares. The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures


References
-
- Ikuta KS, Swetschinski LR, Robles Aguilar G, Sharara F, Mestrovic T, Gray AP, et al. . Global mortality associated with 33 bacterial pathogens in 2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. (2022) 400:2221–48. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02185-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Congdon ST, Guaglione JA, Ricketts OMA, Murphy KV, Anderson MG, Trowbridge DA, et al. . Prevalence and antibiotic resistance of Staphylococcus aureus associated with a college-aged cohort: life-style factors that contribute to nasal carriage. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2023) 13. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1195758 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

