Virological and serological outcomes in people with HIV-HBV coinfection who had discontinued tenofovir-containing antiretroviral therapy: Results from a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 39981332
- PMCID: PMC11841080
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jve.2024.100574
Virological and serological outcomes in people with HIV-HBV coinfection who had discontinued tenofovir-containing antiretroviral therapy: Results from a prospective cohort study
Abstract
Background and aims: Given advances in antiretroviral therapy (ART), some people with HIV are transitioned to non-tenofovir-containing ART; the implications for people with HIV-hepatitis B virus (HBV) are unknown. We characterized HBV-related outcomes in people with HIV-HBV coinfection while not taking tenofovir-containing ART.
Methods: We analyzed participants from the French HIV-HBV Cohort Study in three treatment groups: (1) continuous tenofovir; (2) discontinued tenofovir; (3) never initiated tenofovir. We examined virological and clinical characteristics during follow-up. We assessed determinants of HBV DNA >2000 IU/mL and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) >2x upper limit of normal separately while participants were off tenofovir using univariable logistic regression with generalized estimating equations.
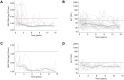
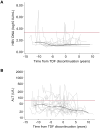
Results: Among 192 participants, 161 (83.9 %) were on continuous tenofovir, 22 (11.5 %) discontinued tenofovir, and 9 (4.7 %) never initiated tenofovir during a median follow-up of 14.5 years (IQR = 10.5-14.8). The median proportion of within-participant visits with undetectable HBV DNA was 96.0 % (IQR = 75.0-100) in the continuous group, 100 % (IQR = 84.0-100) in the discontinued tenofovir group (while off tenofovir), and 100 % (IQR = 95.2-100) in the never initiated tenofovir group. Determinants of HBV DNA >2000 IU/mL while people were off tenofovir were detectable HIV RNA (p = 0.041), lower CD4+ T-cell count (p = 0.027), HBeAg positive serology (p = 0.004) and positive hepatitis D serology (p = 0.001). ALT elevation was associated with positive hepatitis C antibody serology (p = 0.012).
Conclusions: This proof-of-concept study shows that selected people with HIV-HBV coinfection may not lose virologic control of HBV when off tenofovir. HBV virologic activity while off tenofovir may be more closely associated with uncontrolled HIV infection and positive HBeAg serology.
Keywords: HIV; Hepatitis B; Tenofovir; Treatment simplification; Virus replication.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships that may be considered as potential competing interests: Karine Lacombe reports a relationship with Gilead Sciences Inc, MSD Merck Sharp & Dohme AG, and ViiV Healthcare. Anders Boyd reports a relationship with Gilead Sciences Inc that includes speaking and lecture fees. All other authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

