SOX10-Mediated Regulation of Enteric Glial Phenotype in vitro and its Relevance for Neuroinflammatory Disorders
- PMID: 39982575
- PMCID: PMC11845537
- DOI: 10.1007/s12031-025-02321-y
SOX10-Mediated Regulation of Enteric Glial Phenotype in vitro and its Relevance for Neuroinflammatory Disorders
Abstract
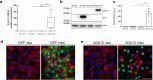
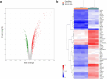
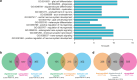
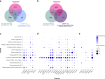
The transcription factor SOX10 is a key regulator of myelinated glial cell phenotype and function, with a known role in multiple sclerosis (MS). SOX10 is also expressed in enteric glial cells (EGC) within the gut, yet its regulatory functions in EGC remain poorly understood. This study aimed to identify SOX10 target genes that influence EGC phenotype and may have implications for MS. An EGC cell line was established for doxycycline-inducible SOX10 overexpression. Impact of SOX10 overexpression on EGC phenotype was assessed by genome-wide expression analysis and results were validated via RT-qPCR and western blot. Data were compared with SOX10 ChIP-seq and transcriptomic datasets from MS patients to identify pan-glial SOX10 target genes potentially linked to neuroinflammatory disorders. SOX10 overexpression was associated with ectopic upregulation of genes related to myelin regulation and glial differentiation, as evidenced by increased PLP1 expression at mRNA and protein levels. Comparison to ChIP-seq and MS datasets highlight SOX10 target genes, including PLP1, RNF130, NES and APOD potentially involved in central and peripheral manifestations of MS pathology. Our findings support a cell-specific regulation of EGC phenotype through SOX10 expression level and identify SOX10-regulated genes relevant to EGC function. This research advances the understanding of EGC diversity and provide information about glial cells targeting in neuroinflammatory disorders.
Keywords: Enteric glial cells; Multiple sclerosis; Nestin; Neuroinflammation; PLP1; Schwann cell; Sox10.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of Interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Stringent comparative sequence analysis reveals SOX10 as a putative inhibitor of glial cell differentiation.BMC Genomics. 2016 Nov 7;17(1):887. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3167-3. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27821050 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic interaction between Sox10 and Zfhx1b during enteric nervous system development.Dev Biol. 2010 May 15;341(2):416-28. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.02.036. Epub 2010 Mar 4. Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20206619
-
Regulation of intestinal epithelial cells transcriptome by enteric glial cells: impact on intestinal epithelial barrier functions.BMC Genomics. 2009 Nov 2;10:507. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-507. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19883504 Free PMC article.
-
The role of SOX10 during enteric nervous system development.Dev Biol. 2013 Oct 1;382(1):330-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.04.024. Epub 2013 May 2. Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23644063 Review.
-
Comparative role of SOX10 gene in the gliogenesis of central, peripheral, and enteric nervous systems.Differentiation. 2022 Nov-Dec;128:13-25. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2022.09.001. Epub 2022 Sep 23. Differentiation. 2022. PMID: 36198237 Review.
References
-
- Baghdadi MB, Ayyaz A, Coquenlorge S et al (2022) Enteric glial cell heterogeneity regulates intestinal stem cell niches. Cell Stem Cell 29:86-100.e6. 10.1016/j.stem.2021.10.004 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

